[RTD400 LLD]K344 ADC SW+HW trigger
1. Abstract 1. 摘要
The S32K344 ADC is a SAR ADC with a resolution which can up to 14 bits. It has a variety of software and hardware triggering methods, supports various external trigger sources, and introduces BCTU so that the trigger resources can be externally connected to multi-channel EMIOS and TRIGMUX, adding more ADC trigger sources. This article mainly explains the following ADC software and hardware triggering methods, and provides supporting codes.
S32K344 ADC 是一个分辨率最高可达 14 位的 SAR ADC。它具有多种软件和硬件触发方法,支持多种外部触发源,并引入了 BCTU,使得触发资源可以外部连接到多通道 EMIOS 和 TRIGMUX,增加更多的 ADC 触发源。本文主要解释了以下 ADC 的软件和硬件触发方法,并提供了支持代码。

Fig 1 图 1
It is mainly divided into 5 parts:
它主要分为 5 部分:
(1) SW+ADC: software trigger, by adding timer PIT, the software trigger ADC is called regularly to complete channel sampling, and the collected value is printed out through UART printf.
(1) SW+ADC: 软件触发,通过添加定时器 PIT,软件触发 ADC 定期被调用以完成通道采样,并通过 UART printf 输出收集到的值。
(2) SW+BCTU+ADC: software trigger, by adding timer PIT, the software trigger BTCU is called regularly to complete ADC channel sampling, and the collected value is printed out through UART printf.
(2) SW+BCTU+ADC: 软件触发,通过添加定时器 PIT,定期调用软件触发 BCTU 完成 ADC 通道采样,并通过 UART printf 输出收集到的值。
(3) PIT+TRIGMUX+ADC: hardware trigger, connect PIT to ADC through TRIGMUX, trigger ADC channel sampling through PIT hardware, and print the conversion value after the sampling conversion is completed.
(3) PIT+TRIGMUX+ADC: 硬件触发,通过 TRIGMUX 将 PIT 连接到 ADC,通过 PIT 硬件触发 ADC 通道采样,并在采样转换完成后打印转换值。
(4) EMIOS+BCTUHW+ADC: hardware trigger, through EMIOS timing trigger BCTU to complete the corresponding ADC single channel sampling, due to the high sampling rate, only the BCTU sampling value is printed regularly.
(4) EMIOS+BCTUHW+ADC: 硬件触发,通过 EMIOS 定时触发 BCTU 完成相应的 ADC 单通道采样,由于采样率较高,仅定期打印 BCTU 的采样值。
(5) EMIOS+BCTUHWLIST+ADC: hardware trigger, through EMIOS timing trigger BCTU to complete ADC list channel sampling, due to the high sampling rate, the list channel value sampled by BCTU is printed regularly.
(5) EMIOS+BCTUHWLIST+ADC: 硬件触发,通过 EMIOS 定时触发 BCTU 完成 ADC 列表通道采样,由于采样率较高,BCTU 采样的列表通道值会定期打印。
2. ADC SW HW Trigger
2.1 Hardware and software platform
2.1 硬件和软件平台
SW: RTD400 LLD,S32DS3.5
HW:S32K3X4EVB-T172
2.2 SW+ADC software trigger
2.2 SW+ADC 软件触发
In fact, the original ADC demo of RTD400 already has ADC software and BCTU software trigger. This article adds PIT timing software trigger based on this function, and prints it out through UART printf, making it more convenient to check the ADC test value through serial port printing.
事实上,RTD400 的原始 ADC 演示已经具备了 ADC 软件和 BCTU 软件触发的功能。本文在此基础上增加了 PIT 定时软件触发,并通过 UART printf 输出,使得通过串口打印检查 ADC 测试值更加方便。
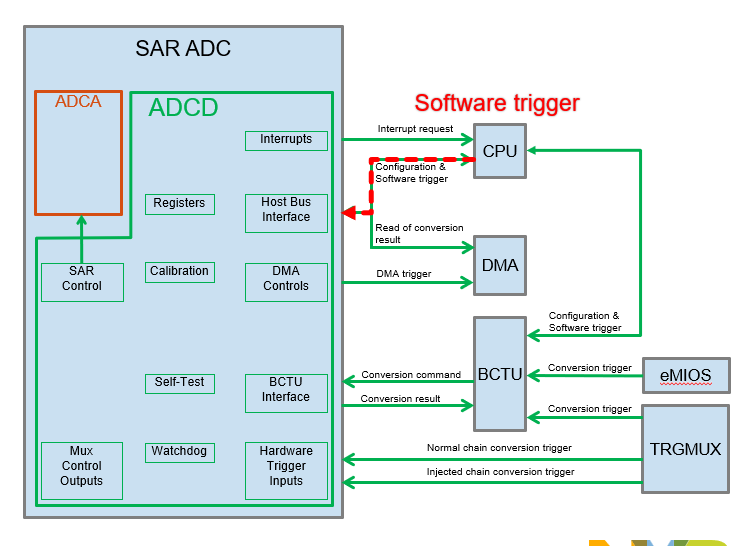
The block diagram structure of the software triggering ADC in this article is as follows:
本文中软件触发 ADC 的块图结构如下:
Fig 2 图 2
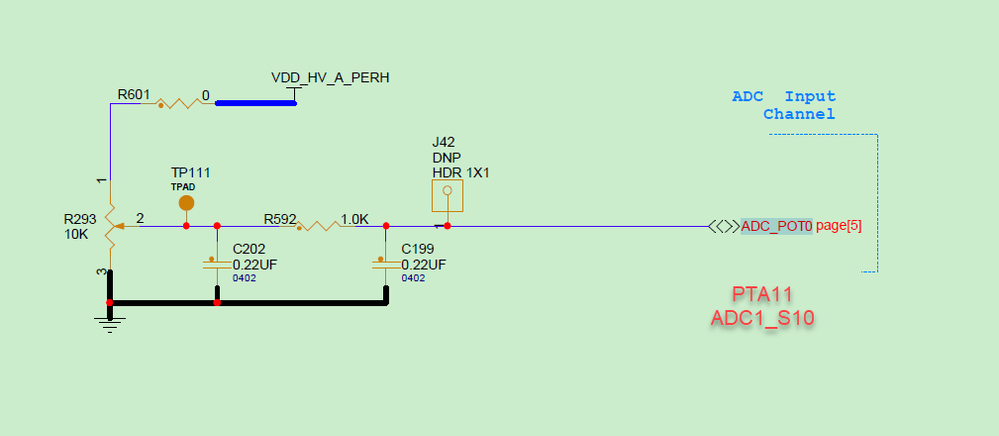
The S32K344EVB board has a potentiometer connected to ADC1_S10, PTA11:
The S32K344EVB 板将电位器连接到 ADC1_S10,PTA11:
Fig 3 图 3
Therefore, the software trigger in this section is mainly used to collect ADC1_S10. The UART printing port uses the serial port of the onboard emulator: LPUART6_RX PTA15, LPUART6_TX PTA16, with a baud rate of 115200.
因此,本节中的软件触发主要用于收集 ADC1_S10。UART 打印端口使用片上仿真器的串口:LPUART6_RX PTA15,LPUART6_TX PTA16,波特率为 115200。
For the software trigger demo in this article, the main configuration involves the following modules:
对于本文中软件触发示例的主要配置涉及以下模块:
(1)Pins: (1)引脚:
Fig 4 图 4
ADC1_s10: PTA11 is the voltage of the onboard potentiometer to be tested, which is adjustable.
ADC1_s10: PTA11 是待测试的内部电位器的电压,可调。
PTA29: Connect the onboard D13 red light to test the PIT timer interrupt and enter the flashing state, used as the breathing light of the PIT.
PTA29: 将内置的 D13 红色 LED 连接起来测试 PIT 定时器中断,并进入闪烁状态,用作 PIT 的呼吸灯。
PTA16: UART6_TX, used to send the collected ADC value.
PTA16: UART6_TX,用于发送采集的 ADC 值。
(2)clocks (2)钟表
Used to configure the system clock. You need to pay attention to the UART6 clock source of 40Mhz, the ADC1 clock source of 160Mhz, and the PIT0 clock source of 40Mhz
用于配置系统时钟。需要注意 UART6 的时钟源为 40MHz,ADC1 的时钟源为 160MHz,以及 PIT0 的时钟源为 40MHz。
(3)Peripherals (3)外设
Involved peripheral modules Siul2_Port,Siul2_Dio, Pit, Lpuart_Uart, Adc_Sar_Ip, IntCtrl_Ip.
涉及的外围模块 Siul2_Port, Siul2_Dio, Pit, Lpuart_Uart, Adc_Sar_Ip, IntCtrl_Ip。
Siul2_Port: Add 4 pins ADC PTA11 MSCR 11, RED LED PTA29 MSCR 29, UART6_RX PTA15 MSCR 15, UART6_RX PTA16 MSCR 16.
Siul2_Port: 添加 4 个引脚 ADC PTA11 MSCR 11,RED LED PTA29 MSCR 29,UART6_RX PTA15 MSCR 15,UART6_RX PTA16 MSCR 16。
Siul2_Dio: Add the module mainly to allow related API functions to come in, so as to control GPIO pins.
Siul2_Dio: 主要添加该模块以引入相关 API 功能,从而控制 GPIO 引脚。
Pit: Used to generate 1S timing, the main configuration is as follows:
Pit: 用于生成 1S 定时,主要配置如下:
Fig 5 图 5
Fig 6 图 6
Lpuart_Uart:
Fig 7 图 7
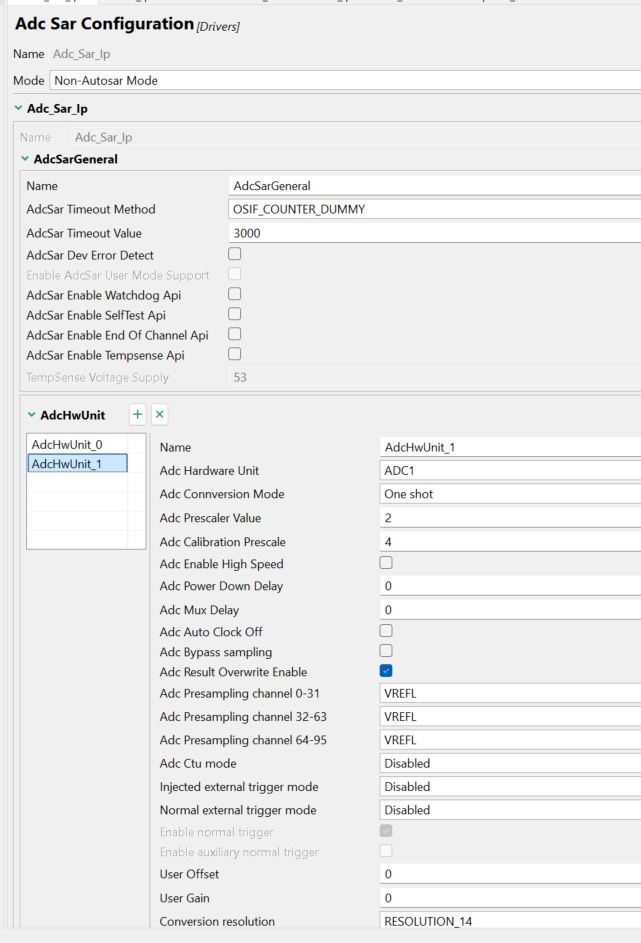
Adc_Sar_Ip:
Fig 8 图 8

Fig 9 图 9
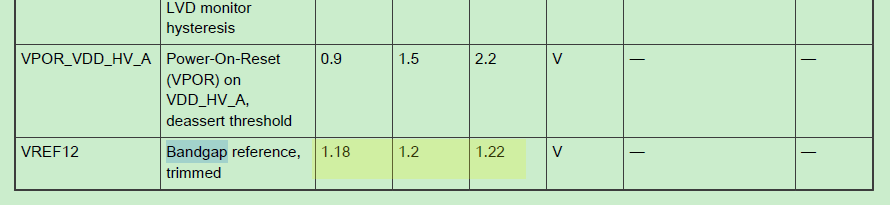
It should be noted here that ADC calibration prescale and Adc prescaler vale need to meet the following conditions, which can be found on S32K3RM:
应注意这里,ADC 校准分频器和 Adc 预分频器值需要满足以下条件,这些内容可以在 S32K3RM 中找到:
Fig 10 图 10
Since the clock source of ADC1 is 160MHz, the calibration division is configured as 4 and the conversion division is configured as 2.
由于 ADC1 的时钟源为 160MHz,校准分频配置为 4,转换分频配置为 2。
IntCtrl_Ip:
Fig 11 图 11
The purpose is to open the interrupt of PIT and LPUART6, and register the corresponding handler.
目的是打开 PIT 和 LPUART6 的中断,并注册相应的处理程序。
CT configuration is completed, and the code is generated. Next, move to the main function and add the following code:
CT 配置已完成,并生成了代码。接下来,移动到主函数并添加以下代码:
void AdcEndOfChainNotif1(void)
{
notif_triggered1 = TRUE;
data1 = Adc_Sar_Ip_GetConvData(ADCHWUNIT_1_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE, 34);
/* Checks the measured ADC data conversion */
// while (ADC_TOLERANCE(data, ADC_BANDGAP));
}
void Pit0ch0Notification(void)
{
toggleLed = 1U;
Siul2_Dio_Ip_TogglePins(LED_Q172_PORT, (1<<LED_Q172_PIN));
}
int main(void)
{
StatusType status;
uint8 Index;
Clock_Ip_StatusType clockStatus;
/* Initialize and configure drivers */
clockStatus = Clock_Ip_Init(&Clock_Ip_aClockConfig[0]);
while (clockStatus != CLOCK_IP_SUCCESS)
{
clockStatus = Clock_Ip_Init(&Clock_Ip_aClockConfig[0]);
}
Siul2_Port_Ip_Init(NUM_OF_CONFIGURED_PINS_PortContainer_0_BOARD_InitPeripherals, g_pin_mux_InitConfigArr_PortContainer_0_BOARD_InitPeripherals);
/* set PIT 0 interrupt */
IntCtrl_Ip_Init(&IntCtrlConfig_0);
IntCtrl_Ip_EnableIrq(PIT0_IRQn);
status = (StatusType) Adc_Sar_Ip_Init(ADCHWUNIT_1_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE, &AdcHwUnit_1_BOARD_InitPeripherals);
while (status != E_OK);
IntCtrl_Ip_InstallHandler(ADC1_IRQn, Adc_Sar_1_Isr, NULL_PTR);
IntCtrl_Ip_EnableIrq(ADC1_IRQn);
for(Index = 0; Index <= 5; Index++)
{
status = (StatusType) Adc_Sar_Ip_DoCalibration(ADCHWUNIT_1_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE);
if(status == E_OK)
{
break;
}
}
Adc_Sar_Ip_EnableNotifications(ADCHWUNIT_1_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE, ADC_SAR_IP_NOTIF_FLAG_NORMAL_ENDCHAIN | ADC_SAR_IP_NOTIF_FLAG_INJECTED_ENDCHAIN);
/* Initialize PIT instance 0 - Channel 0 */
Pit_Ip_Init(PIT_INST_0, &PIT_0_InitConfig_PB_BOARD_InitPeripherals);
/* Initialize channel 0 */
Pit_Ip_InitChannel(PIT_INST_0, PIT_0_CH_0);
/* Enable channel interrupt PIT_0 - CH_0 */
Pit_Ip_EnableChannelInterrupt(PIT_INST_0, CH_0);
/* Start channel CH_0 */
Pit_Ip_StartChannel(PIT_INST_0, CH_0, PIT_PERIOD);
Lpuart_Uart_Ip_Init(UART_LPUART_INTERNAL_CHANNEL, &Lpuart_Uart_Ip_xHwConfigPB_6_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS);
printf("S32K344 PIT TRIGMUX ADC demo RTD400.\r\n");
while(1)
{
#if 1
if( toggleLed == 1)
{
toggleLed = 0;
/* Start a SW triggered normal conversion on ADC_SAR */
Adc_Sar_Ip_StartConversion(ADCHWUNIT_1_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE, ADC_SAR_IP_CONV_CHAIN_NORMAL);
/* Wait for the notification to be triggered and read the data */
while (notif_triggered1 != TRUE);
notif_triggered1 = FALSE;
printf("ADC1_s10 ch34 data = %d .\r\n", data1);
}
#endif
}
}
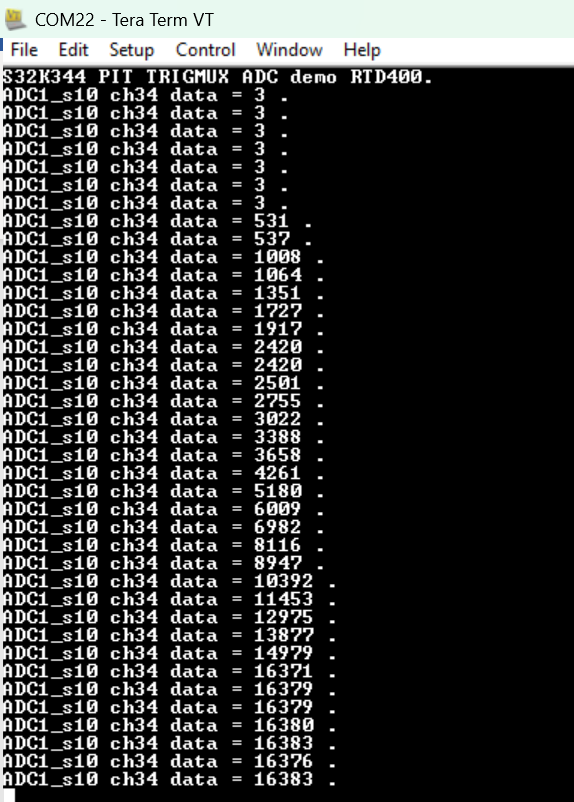
The test results are printed as follows:
测试结果如下打印:
Fig 12 图 12
This section content supporting code: S32K344_PIT_SW_ADC_RTD400.zip
2.3 SW+BCTU+ADC Software trigger BCTU
2.3 SW+BCTU+ADC 软件触发 BCTU
Based on SW+ADC trigger, add BCTU, and use BCTU software trigger to complete ADC sampling. The block diagram structure is as follows:
基于 SW+ADC 触发,添加 BCTU,并使用 BCTU 软件触发完成 ADC 采样。块图结构如下:
Fig 13 图 13
This section uses BCTU software to trigger ADC0 sampling. The sampling channel does not actually use external pin input, but collects the bandgap value of ADC0. The software trigger calls the software trigger function through the PIT 1S cycle, and prints the ADC sampling conversion value to UART after completion.
此部分使用 BCTU 软件触发 ADC0 采样。采样通道实际上不使用外部引脚输入,而是收集 ADC0 的基准电压值。软件触发调用 PIT 1S 周期的软件触发功能,并在完成后将 ADC 采样转换值打印到 UART。
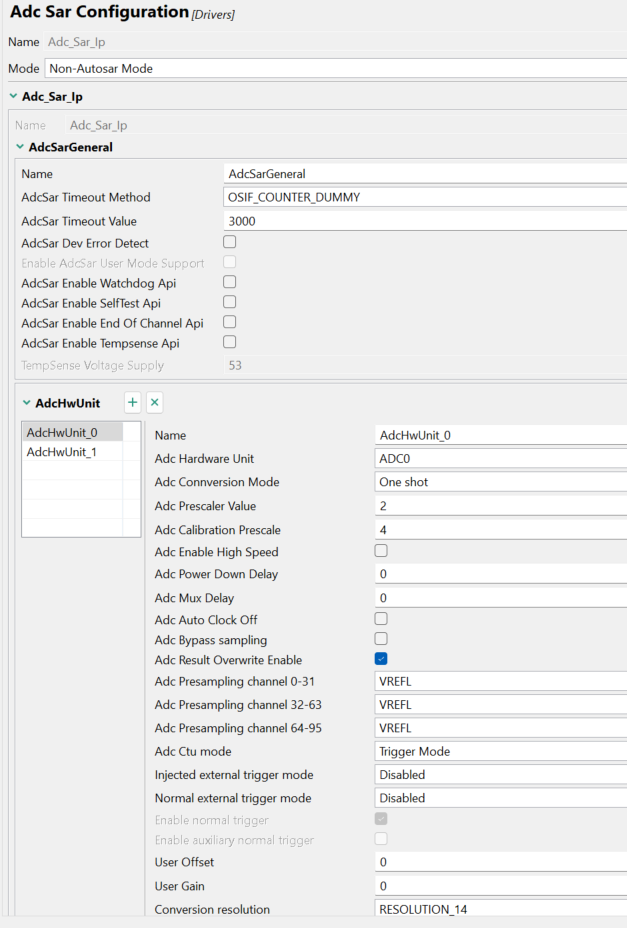
In the CT tool, the main modification points are peripherals, adding ADC0 in adc_sar_lp, and configuring it as BCTU trigger.
在 CT 工具中,主要的修改点是外设,即在 adc_sar_lp 中添加 ADC0,并将其配置为 BCTU 触发器。
Fig 14 图 14
Fig 15 图 15
Here we can see that in Figure 14, the adc ctu mode is: trigger mode.
在这里我们可以看到在图 14 中,adc ctu 模式为:触发模式。
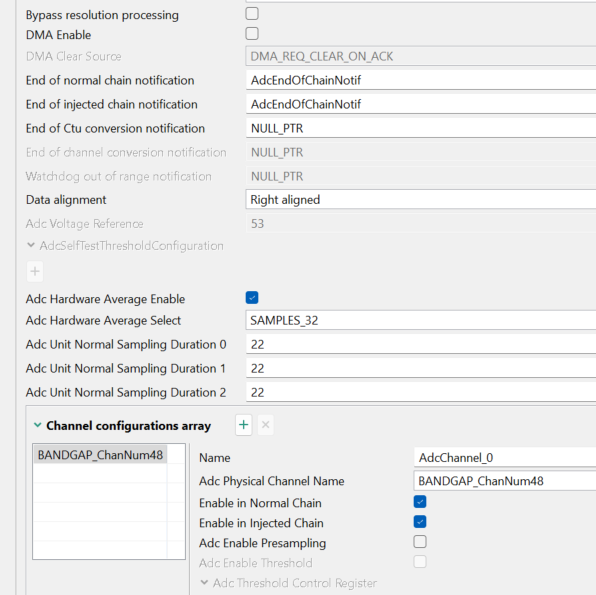
Add the Bctu_Ip module and configure it as follows:
添加 Bctu_Ip 模块并按如下配置:
Fig 16 图 16
The corresponding selected BCTU channel is 48, which corresponds to the internal bandgap module.
对应的选定 BCTU 通道是 48,这对应于内部带隙模块。
Fig 17 图 17
The typical value is 1.2V, so the reference voltage is 5V, and the corresponding 14-bit ADC bandgap expected value is:
典型的值是 1.2V,所以参考电压是 5V,相应的 14 位 ADC 基准电压期望值是:
(2^14)*1.2/5=3932 around.
(2^14)*1.2/5=3932 左右。
After completing the CT configuration code generation, add the following code in main.c:
在完成 CT 配置代码生成后,在 main.c 中添加以下代码:
void AdcEndOfChainNotif(void)
{
notif_triggered = TRUE;
data = Adc_Sar_Ip_GetConvData(ADCHWUNIT_0_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE, ADC_SAR_USED_CH);
}
void Pit0ch0Notification(void)
{
toggleLed = 1U;
Siul2_Dio_Ip_TogglePins(LED_Q172_PORT, (1<<LED_Q172_PIN));
}
void BctuWatermarkNotif(void)
{
uint8 idx;
notif_triggered = TRUE;
for (idx = 0u; idx < BCTU_FIFO_WATERMARK; idx++)
{
data_bctu = Bctu_Ip_GetFifoData(BCTUHWUNIT_0_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE, BCTU_USED_FIFO_IDX);
}
}
int main(void)
{
StatusType status;
uint8 Index;
Clock_Ip_StatusType clockStatus;
/* Initialize and configure drivers */
clockStatus = Clock_Ip_Init(&Clock_Ip_aClockConfig[0]);
while (clockStatus != CLOCK_IP_SUCCESS)
{
clockStatus = Clock_Ip_Init(&Clock_Ip_aClockConfig[0]);
}
Siul2_Port_Ip_Init(NUM_OF_CONFIGURED_PINS_PortContainer_0_BOARD_InitPeripherals, g_pin_mux_InitConfigArr_PortContainer_0_BOARD_InitPeripherals);
Bctu_Ip_Init(BCTUHWUNIT_0_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE, &BctuHwUnit_0_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS);
status = (StatusType) Adc_Sar_Ip_Init(ADCHWUNIT_0_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE, &AdcHwUnit_0_BOARD_InitPeripherals);
while (status != E_OK);
/* set PIT 0 interrupt */
IntCtrl_Ip_Init(&IntCtrlConfig_0);
IntCtrl_Ip_EnableIrq(PIT0_IRQn);
/* Install and enable interrupt handlers */
IntCtrl_Ip_InstallHandler(ADC0_IRQn, Adc_Sar_0_Isr, NULL_PTR);
IntCtrl_Ip_InstallHandler(BCTU_IRQn, Bctu_0_Isr, NULL_PTR);
IntCtrl_Ip_EnableIrq(ADC0_IRQn);
IntCtrl_Ip_EnableIrq(BCTU_IRQn);
/* Call Calibration function multiple times, to mitigate instability of board source */
for(Index = 0; Index <= 5; Index++)
{
status = (StatusType) Adc_Sar_Ip_DoCalibration(ADCHWUNIT_0_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE);
if(status == E_OK)
{
break;
}
}
Adc_Sar_Ip_EnableNotifications(ADCHWUNIT_0_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE, ADC_SAR_IP_NOTIF_FLAG_NORMAL_ENDCHAIN | ADC_SAR_IP_NOTIF_FLAG_INJECTED_ENDCHAIN);
/* Start a SW triggered conversion on BCTU using a single trigger */
Bctu_Ip_SetGlobalTriggerEn(BCTUHWUNIT_0_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE, TRUE);
Bctu_Ip_EnableNotifications(BCTUHWUNIT_0_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE, BCTU_IP_NOTIF_FIFO1);
/* Initialize PIT instance 0 - Channel 0 */
Pit_Ip_Init(PIT_INST_0, &PIT_0_InitConfig_PB_BOARD_InitPeripherals);
/* Initialize channel 0 */
Pit_Ip_InitChannel(PIT_INST_0, PIT_0_CH_0);
/* Enable channel interrupt PIT_0 - CH_0 */
Pit_Ip_EnableChannelInterrupt(PIT_INST_0, CH_0);
/* Start channel CH_0 */
Pit_Ip_StartChannel(PIT_INST_0, CH_0, PIT_PERIOD);
Trgmux_Ip_Init(&Trgmux_Ip_xTrgmuxInitPB);//
Lpuart_Uart_Ip_Init(UART_LPUART_INTERNAL_CHANNEL, &Lpuart_Uart_Ip_xHwConfigPB_6_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS);
printf("S32K344 PIT TRIGMUX ADC demo RTD400.\r\n");
while(1)
{
if( toggleLed == 1)
{
toggleLed = 0;
Bctu_Ip_SwTriggerConversion(BCTUHWUNIT_0_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE, BCTU_USED_SINGLE_TRIG_IDX);
while (notif_triggered != TRUE);
notif_triggered = FALSE;
printf("ADC0_bandgap ch48 data_bctu = %d .\r\n", data_bctu);
}
}
}
Test result:
Fig 18
It is close to the typical expected value, indicating that it has been successfully run.
Used demo code:S32K344_PIT_TRIGMUX_BCTUSW_ADC_printf_RTD400.zip
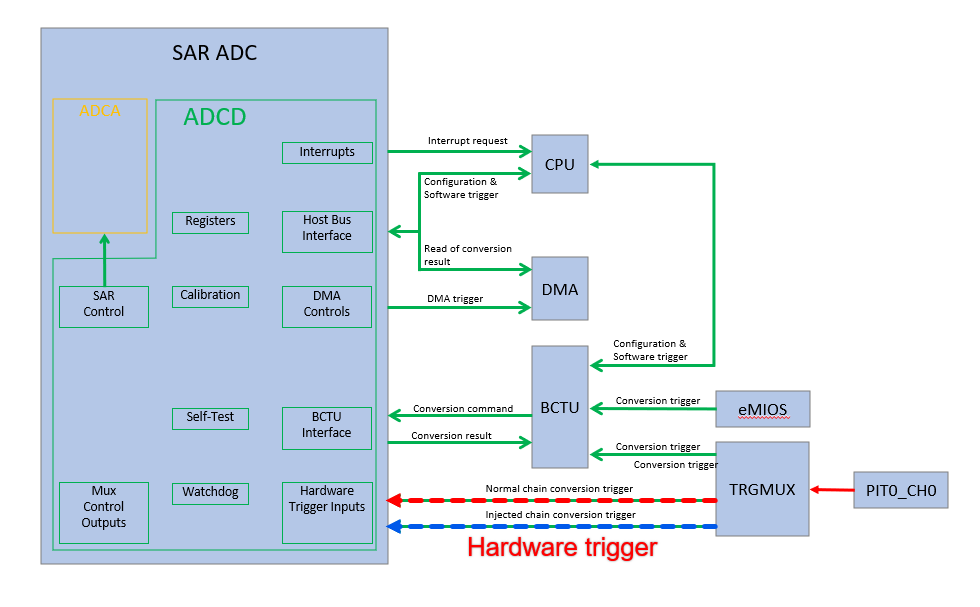
2.4 PIT+TRIGMUX+ADC hardware PIT TRIGUMX trigger
This section is about hardware triggering. PIT is used in combination with TRIGMUX to directly trigger ADC1 channel 34, i.e. ADC1_S10 sampling. The trigger structure diagram is as follows:
Fig 19
Also based on the previous code, you need to add an additional module Trgmux_Ip in the CT peripherals, and the rest of the configuration remains unchanged.
Fig 20
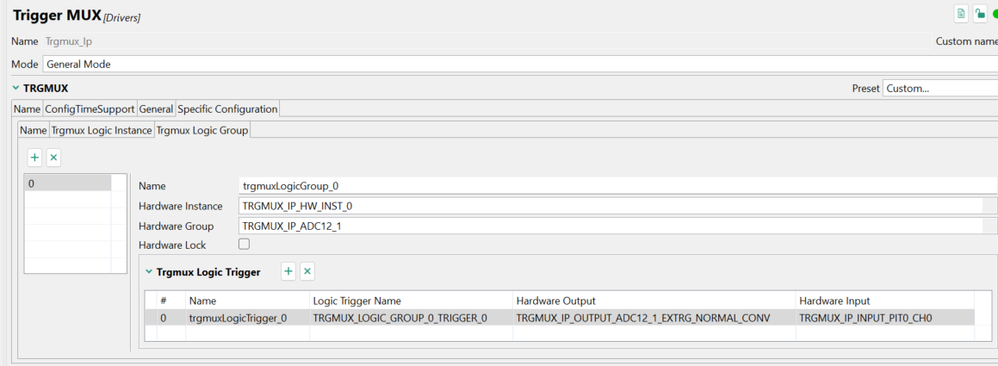
Here, the input of Trigmux is selected as PIT0_CH0 and the output is ADC1.
The code is also much simpler. Add the following code in main:
Trgmux_Ip_Init(&Trgmux_Ip_xTrgmuxInitPB);//
while(1)
{
if(notif_triggered1 == TRUE)
{
notif_triggered1 = FALSE;
printf("ADC1_s10 ch34 data = %d .\r\n", data1);
}
}
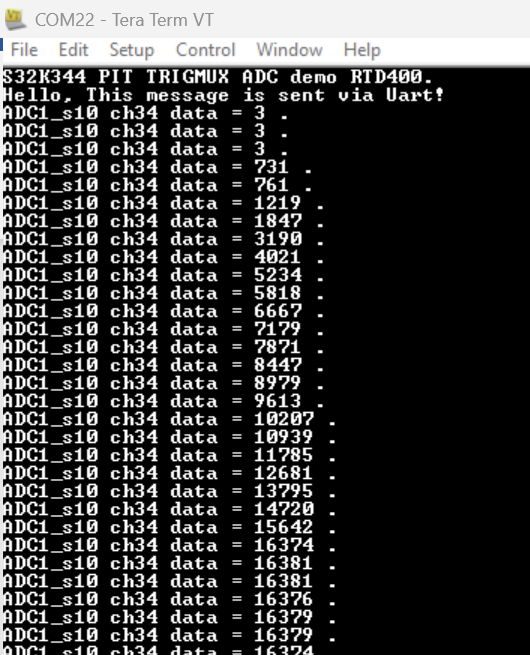
In While(1), we can see that there is no software-triggered call. We can directly check the ADC1 conversion completion flag and then print the data. The test results are as follows:
Fig 21
It can be seen that as the external potentiometer changes, the sampled value of ADC1_S10 also changes.
Used demo:S32K344_PIT_TRIGMUX_ADC_printf_RTD400.zip
2.5 EMIOS+BCTUHW+ADC hardware EMIOS BCTU trigger
The block diagram structure of this section is as follows:
Fig 22
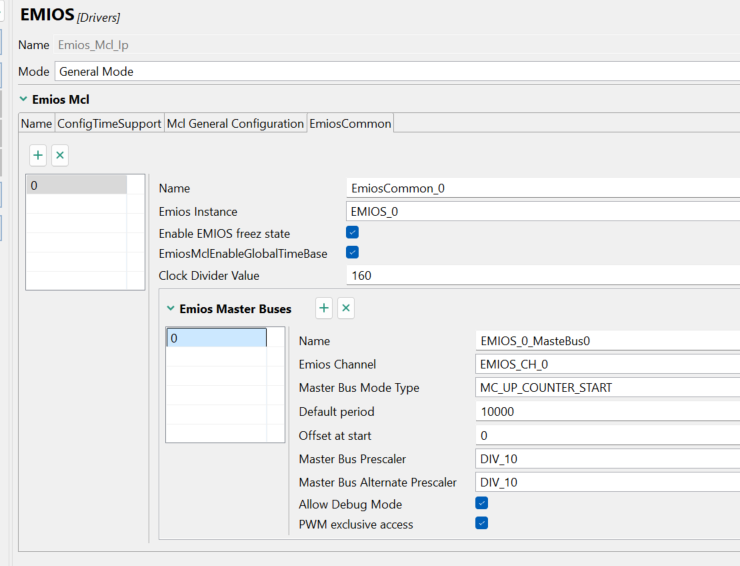
Use eMIOS0_CH0 to generate a 10Khz clock to trigger BCTU to complete the sampling of ADC0_48 channel, that is, bandgap.
In the CT tool, add Emios_Mcal_Ip and configure it as follows:
Fig 23
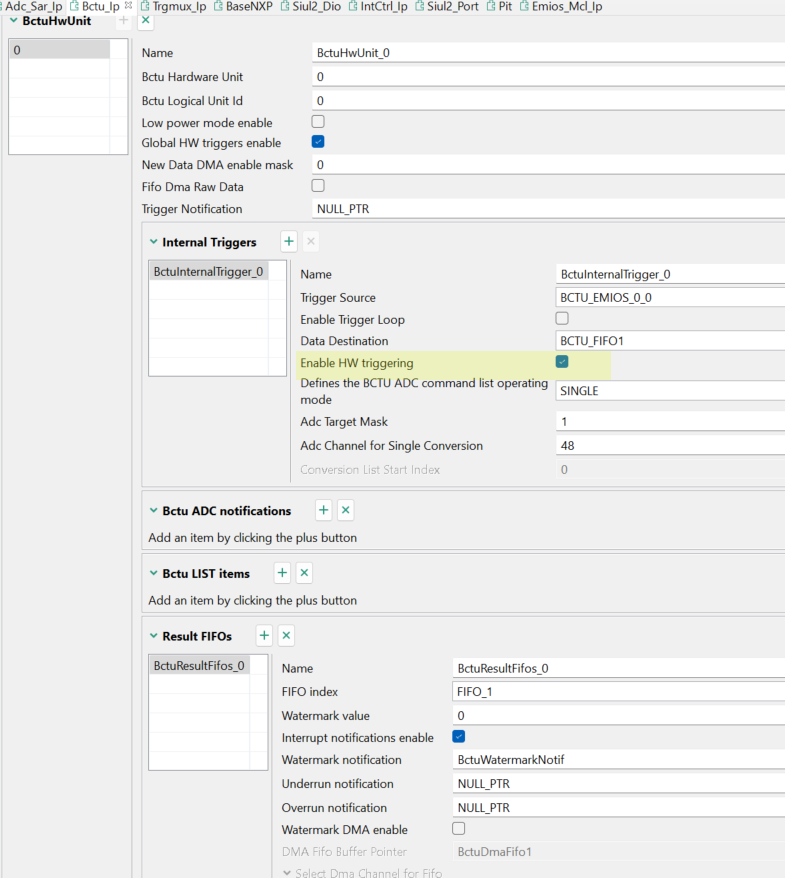
Change the BCTU configuration to enable HW triggering. The configuration is as follows:
Fig 24
Main code related codes are as follows:
Emios_Mcl_Ip_Init(EMIOS_INST0, &Emios_Mcl_Ip_0_Config_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS);
while(1)
{
if( toggleLed == 1)
{
toggleLed = 0;
printf("ADC0_bandgap ch48 data_bctu = %d .\r\n", data_bctu);
}
}
Since the sampling rate is triggered at a frequency of 10Khz, the frequency is relatively fast, so the printing here is still based on 1s. The printing results are as follows:
Fig 25
As you can see, the result is also a variable bandgap value.
Used demo:S32K344_PIT_TRIGMUX_BCTUHW_EMIOS_ADC_printf_RTD400.zip
2.6 EMIOS+BCTUHW LIST+ADC hardware EMIOS BCTU trigger LIST
This section is similar to the EMIOS BCTU hardware trigger above, except that the BCTU is configured in the form of LIST, which can trigger the conversion of multiple channels at once. The main modifications are in the BCTU module:
Fig 26
Add the corresponding main code as follows:
#define BCTU_FIFO_WATERMARK 3U
void BctuWatermarkNotif(void)
{
uint8 idx;
notif_triggered = TRUE;
for (idx = 0u; idx < BCTU_FIFO_WATERMARK; idx++)
{
data_bctu[idx] = Bctu_Ip_GetFifoData(BCTUHWUNIT_0_BOARD_INITPERIPHERALS_INSTANCE, BCTU_USED_FIFO_IDX);
}
}
while(1)
{
if( toggleLed == 1)
{
toggleLed = 0;
printf("ADC0_bandgap ch48 data_bctu = %d .\r\n", data_bctu[0]);
printf("ADC0_vrefl ch54 data_bctu = %d .\r\n", data_bctu[1]);
printf("ADC0_vrefh ch55 data_bctu = %d .\r\n", data_bctu[2]);
}
}
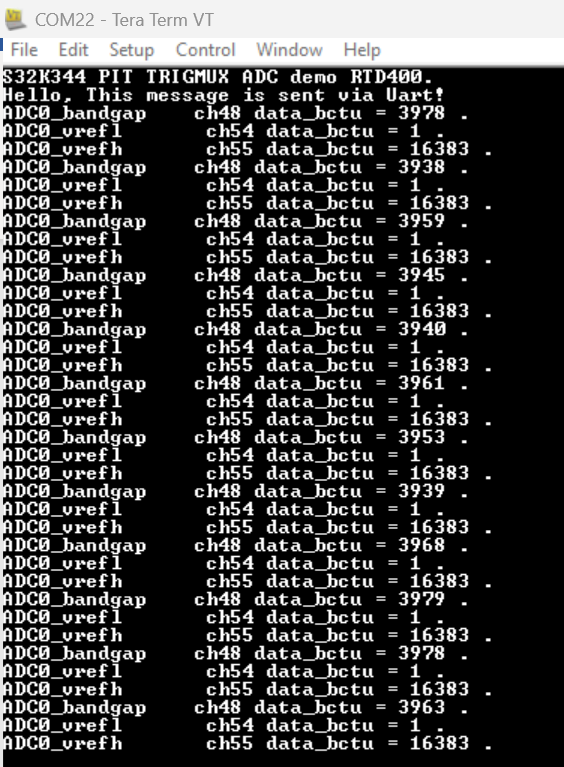
Test result is:
Fig 27
It can be seen that the results are consistent with the collected bandgap, VREFL, and VREFH, indicating that the code function is running normally.
Code in this section:S32K344_PIT_TRIGMUX_BCTUHWLIST_EMIOS_ADC_printf_RTD400.zip