- 1Department of Human Performance and Health, University of South Carolina Upstate, Spartanburg, SC, United States
1 南卡罗来纳大学北部分校人类表现与健康系,美国南卡罗来纳州斯帕坦堡 - 2College of Health, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, United States
2 俄勒冈州立大学健康学院,美国俄勒冈州科瓦利斯
Objective: The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between parent ratings of motor skills and executive function (EF) in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in the United States and Taiwan.
目的: 本研究的目的是检查美国和台湾自闭症谱系障碍 (ASD) 儿童父母运动技能评分与执行功能 (EF) 之间的关系。
Materials and method: One hundred and seventy-two parents/legal guardians of children (4–6 years and 11 months old) with ASD were recruited from two countries, Taiwan (n = 100) and the United States (n = 72). The parents or guardians of the child with ASD completed a questionnaire including demographic information, child’s motor skills (using Children Activity Scale – Parents, ChAS-P), and child’s EF (using Childhood Executive Functioning Inventory, CHEXI). A series of hierarchical multiple regressions were conducted to determine whether ChAS-P (total motor score, fine motor skills, and gross motor skill) was associated with CHEXI (total EF score, working memory, and inhibition), after controlling for covariates (i.e., age, gender, race, body mass index, whether children received physical activity or cognitive training, parental education level).
材料和方法: 从台湾 (n = 100) 和美国 (n = 72) 两个国家招募了 172 名 ASD 儿童 (4-6 岁零 11 个月) 的父母/法定监护人。ASD 儿童的父母或监护人完成了一份问卷,包括人口统计信息、儿童的运动技能(使用儿童活动量表 - 父母,ChAS-P)和儿童的 EF(使用儿童执行功能量表,CHEXI)。进行一系列分层多元回归,以确定在控制协变量 (即年龄、性别、种族、体重指数、儿童是否接受体育活动或认知训练、父母教育水平) 后,ChAS-P (总运动评分、精细运动技能和粗大运动技能) 是否与 CHEXI (总 EF 评分、工作记忆和抑制)相关。
Results: Total motor skills, fine motor skills, and gross motor skills were significantly associated with EF in both working memory and inhibition as rated by parents in both countries (β = 0.21–0.57, p < 0.01), with the exception of a non-significant association between parent-rated total motor skills, fine motor skills, and gross motor skills, and inhibition among Taiwanese children with ASD. In addition, the associations between parent ratings of motor skills (i.e., fine motor and gross motor skills) and EF (i.e., working memory and inhibition) were similar between the two countries.
结果: 根据两国父母的评分,总运动技能、精细运动技能和粗大运动技能在工作记忆和抑制方面与 EF 显著相关 (β = 0.21-0.57,p < 0.01),除了父母评定的总运动技能、精细运动技能和粗大运动技能与台湾 ASD 儿童的抑制之间无显著关联。此外,父母对运动技能 (即精细运动和粗大运动技能) 和 EF (即工作记忆和抑制) 的评分之间的关联在两个国家之间相似。
Conclusion: Positive associations with specific aspects of parent ratings of fine motor and gross motor skills and working memory and inhibition were found in children with ASD from both countries. These findings have implications for future interventions and programs focused on improving early motor skills and EF development for young children with ASD from Taiwan and the United States.
结论: 在这两个国家的 ASD 儿童中,发现与父母对精细运动和粗大运动技能以及工作记忆和抑制的评分的特定方面呈正相关。这些发现对未来专注于提高台湾和美国 ASD 幼儿早期运动技能和 EF 发展的干预措施和计划具有意义。
Introduction 介绍
Early childhood is a crucial period for the holistic development of a child’s social, emotional, cognitive, and physical needs to build a solid and broad foundation for lifelong learning and wellbeing (1). Young children above 5 years old experience considerable environmental changes as they move from preschool or home-based care into a more formal school setting like kindergarten. These changes include that young children interact with peers and teachers and are introduced to structured activities and curriculum, which will increase demands on their social, motor, and executive function (EF) skills (2). For many young children, this transition goes well, but it can be quite challenging and stressful for others, especially those children with autism spectrum disorder (3).
幼儿期是儿童社交、情感、认知和身体需求全面发展的关键时期,为终身学习和福祉奠定坚实而广泛的基础 ( 1)。5 岁以上的幼儿在从学前班或家庭托儿所转移到幼儿园等更正规的学校环境时,会经历相当大的环境变化。这些变化包括幼儿与同龄人和老师互动,并被引入结构化的活动和课程,这将增加对他们的社交、运动和执行功能 (EF) 技能的要求 ( 2)。对于许多年幼的孩子来说,这种转变进展顺利,但对其他人来说可能是相当具有挑战性和压力的,尤其是那些患有自闭症谱系障碍的儿童 ( 3)。
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD), a neurodevelopmental disorder, is defined by deficits in social communication and the presence of restricted or repetitive behaviors (4). Based on the recently revealed estimate from the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the prevalence of ASD in 2020 increased from 1 in 68 to 1 in 36 children (5, 6). Similarly, individuals who identified with ASD in Taiwan increased from 10,160 to 15,750 between the years of 2010–2020 (7). Furthermore, the number of children aged 3 through 5 years served under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act (IDEA) Part B services within the ASD category increased from 7.8 percent in 2012 to 10.8 percent in 2017 (8). The drastic increases in autism prevalence worldwide highlight the growing need for health, education, and social services for this population.
自闭症谱系障碍 (ASD) 是一种神经发育障碍,其定义是社交沟通缺陷以及存在受限或重复行为 ( 4)。根据疾病控制和预防中心 (CDC) 最近披露的估计,2020 年 ASD 的患病率从 1/68 增加到 1/36 儿童 (5, 6)。同样,在 10,160 年至 2010 年期间,台湾患有 ASD 的个体从 15,750 人增加到 2020 人 ( 7)。此外,根据《残疾人教育改进法案》(IDEA) B 部分服务在 ASD 类别中服务的 3 至 5 岁儿童人数从 7.8 年的 2012% 增加到 2017 年的 10.8% ( 8)。全球自闭症患病率的急剧增加凸显了这一人群对健康、教育和社会服务的需求不断增长。
In addition to the core characteristics of ASD, deficits in motor skills have been consistently revealed in research on children with ASD (9, 10). “Motor skills” in the present study are defined using the term motor competence, which reflects various global terminologies (i.e., motor proficiency, motor performance, fundamental motor skill, and fine and gross motor skills) to describe goal-directed human movement (11). A myriad of studies have indicated that children with ASD demonstrate impaired or delayed motor skills, including postural control, motor coordination, and fine and gross motor skill (12–15). Evidence has suggested that 87% of children with ASD demonstrated significant motor impairment (16). Landa & Garrett-Mayer (17) indicated that children at higher risk for ASD at 14 months of age demonstrated evident motor skills deficits compared with peers without ASD. A recent meta-analysis further echoed Landa and Garrett-Mayer’s (17) hallmark research and indicated that infants with ASD exhibited motor behavior deficits early on, compared to infants without ASD, and this difference between the two groups amplified as age increased (18). Thus, it is essential to evaluate motor skills among young children with ASD and identify approaches to mitigate this developmental deficit.
除了 ASD 的核心特征外,在对 ASD 儿童的研究中也一致揭示了运动技能的缺陷 (9, 10)。本研究中的“运动技能”使用术语运动能力进行定义,它反映了各种全球术语(即运动熟练度、运动表现、基本运动技能以及精细和粗大运动技能)来描述以目标为导向的人类运动 ( 11)。大量研究表明,ASD 儿童表现出运动技能受损或延迟,包括姿势控制、运动协调以及精细和粗大运动技能 (12-15)。有证据表明,87% 的 ASD 儿童表现出明显的运动障碍 ( 16)。Landa&Garrett-Mayer(17)表示,与没有ASD的同龄人相比,14个月大时ASD风险较高的儿童表现出明显的运动技能缺陷。最近的一项荟萃分析进一步呼应了 Landa 和 Garrett-Mayer (17) 的标志性研究,并表明与没有 ASD 的婴儿相比,患有 ASD 的婴儿在早期就表现出运动行为缺陷,并且两组之间的这种差异随着年龄的增长而放大 ( 18)。因此,必须评估患有 ASD 的幼儿的运动技能并确定减轻这种发育缺陷的方法。
Another commonly impaired developmental area in children with ASD is EF (19, 20). EF refers to a set of higher-order cognitive processes necessary for goal-directed behavior, including inhibitory control, cognitive flexibility, and working memory (21). EF deficits have consistently been reported in children with ASD (22–25). Research has shown that children with ASD demonstrated EF deficits in the performance of planning, inhibition of responses, and self-monitoring compared with their peers without ASD matched on IQ and language level (26). EF is critical to everyday functioning in life (27). If children with ASD experience deficits in EF, it might lead to difficulty in social interaction and quality of life. For example, inhibition, children may not be able to inhibit themselves and show aggressive behavior or distract easily in the class; cognitive flexibility, children may have problems shifting gears and thinking about things in different ways; working memory, children may not be able to hold on and visualize the numbers the teacher has called out. Further, EF deficits observed in individuals with ASD can also result in difficulties later in life, including independent behavior and work functioning (28, 29). Therefore, identifying and assessing EF impairments early in life to prevent long-term difficulties in children with ASD across a range of important functional domains is crucial.
ASD 儿童另一个常见受损的发育区域是 EF ( 19, 20)。EF 是指目标导向行为所必需的一组高阶认知过程,包括抑制控制、认知灵活性和工作记忆 ( 21)。ASD 儿童 (22-25) 的 EF 缺陷一直被报道。研究表明,与智商和语言水平不匹配的 ASD 同龄人相比,患有 ASD 的儿童在计划、抑制反应和自我监控方面的表现表现出 EF 缺陷 ( 26)。EF 对日常生活至关重要 ( 27)。如果 ASD 儿童在 EF 中出现缺陷,可能会导致社交互动和生活质量困难。例如,抑制,孩子可能无法抑制自己并表现出攻击性行为或在课堂上容易分散注意力;认知灵活性,孩子们可能在换档和以不同的方式思考问题时遇到问题;工作记忆,孩子们可能无法坚持和想象老师喊出的数字。此外,在 ASD 患者中观察到的 EF 缺陷也会导致以后的生活困难,包括独立行为和工作功能 (28, 29)。因此,在生命早期识别和评估 EF 损伤以防止 ASD 儿童在一系列重要功能领域出现长期困难至关重要。
In the past, motor skills and EF were regarded as two different constructs developing independently and discussed separately (30). Recent evidence, however, has indicated that these two constructs are interrelated (31, 32). For example, one study found that visual-motor integration skills of preschoolers aged 3 to 5 years significantly predicted their EF skills 7 months after (33). In addition, a systematic review of 21 studies suggested that complex motor skills, which were categorized to have a higher cognitive demand, demonstrated the strongest associations with higher-order cognitive skills (i.e., EF) among children without ASD (34). In the ASD population, evidence for the relationship between motor skills and EF has only been found in a couple of studies (35, 36). Schurink et al. (36) indicated that fine motor skills and balance were significantly correlated with cognitive flexibility among school-aged children with ASD. While the research mentioned above has indicated promising results, these studies have mainly focused on children in western countries such as Europe and the United States. Thus, how these relationships persist or differ in other countries and regions is important to understand.
过去,运动技能和 EF 被视为独立发展的两种不同结构,并单独讨论 ( 30)。然而,最近的证据表明,这两个结构是相互关联的 ( 31, 32)。例如,一项研究发现,3 至 5 岁学龄前儿童的视觉运动整合技能在 7 个月后显着预测了他们的 EF 技能 ( 33)。此外,对 21 项研究的系统评价表明,被归类为具有较高认知需求的复杂运动技能与无 ASD 儿童的高阶认知技能(即 EF)的关联最强 ( 34)。在 ASD 人群中,仅在几项研究中发现了运动技能与 EF 之间关系的证据 ( 35, 36)。Schurink 等人 ( 36) 表明,在 ASD 学龄儿童中,精细运动技能和平衡与认知灵活性显著相关。虽然上述研究表明了有希望的结果,但这些研究主要集中在欧美等西方国家的儿童。因此,了解这些关系在其他国家和地区如何持续存在或有所不同非常重要。
Theoretical frameworks and neurobiological evidence provide the fundamental viewpoint of the co-occurrence and relationship between motor skills and cognitive development (37–39). The theoretical framework of learning to learn proposes that motor behaviors play an essential role in early learning (40). Within this framework, infants demonstrate their abilities to discover new solutions to solve novel problems through their motor flexibility when exploring and interacting with their surroundings. Thus, within this framework, early motor behaviors set the foundation for cognitive development and higher-order cognitive process (i.e., EF). In addition, research has shown that the pre-frontal cortex and cerebellum are co-activating while individuals are performing cognitive and motor tasks (41). Furthermore, the peak developmental age of both motor and cognitive skills in early childhood is around the same timeframe between the ages of 5 to 10 years (42). Therefore, examining the relationships between motor skills and EF early is critical given the evidence of theorized and the neurocognitive associations between the two domains.
理论框架和神经生物学证据提供了运动技能和认知发展之间共存和关系的基本观点 ( 37-39)。学会学习的理论框架提出,运动行为在早期学习中起着至关重要的作用 ( 40)。在这个框架内,婴儿在探索周围环境并与之互动时,通过他们的运动灵活性展示了他们发现新解决方案以解决新问题的能力。因此,在这个框架内,早期运动行为为认知发展和高阶认知过程(即 EF)奠定了基础。此外,研究表明,当个体执行认知和运动任务时,前额叶皮层和小脑会共同激活 ( 41)。此外,幼儿期运动和认知技能的发育高峰年龄大致在 5 至 10 岁之间的同一时间范围内 ( 42)。因此,鉴于理论化的证据和两个领域之间的神经认知关联,早期检查运动技能和 EF 之间的关系至关重要。
Given that both motor and EF development are known to be influenced by the cultural context in which children grow up (43), a more comprehensive understanding of potential cross-cultural similarities or differences in motor skills and EF in children with ASD may significantly contribute to the global perspective on these critical aspects of development, particularly in the context of both Western and Eastern cultures. It is important to note that existing research has revealed noteworthy variations in motor skills and EF between children without ASD in Western and Eastern countries (44, 45). In motor skills comparisons, for instance, Chow et al. (44) utilized a performance-based motor skills assessment and found that Chinese children exhibited better fine motor skills performance, while American children demonstrated superior object control skills. In another study, the motor skills of 255 preschool children aged 4 to 6 from Hong Kong and 544 from Taiwan were assessed, and their performance on the Movement Assessment Battery (MABC) was compared to the standardized data from American children of the same age. The findings revealed statistically significant differences in MABC scores among typically developing children from Hong Kong, Taiwan, and the Unites States, indicating that Chinese children exhibited poorer performance (46).
鉴于已知运动和 EF 发展都受到儿童成长文化背景的影响 ( 43),更全面地了解 ASD 儿童运动技能和 EF 的潜在跨文化相似或差异可能会显着有助于全球视角看待这些关键的发展方面,特别是在西方和东方文化的背景下。值得注意的是,现有研究表明,西方和东方国家没有 ASD 的儿童在运动技能和 EF 方面的显着差异 ( 44, 45)。例如,在运动技能比较中,Chow 等人 ( 44) 利用了基于表现的运动技能评估,发现中国儿童表现出更好的精细运动技能表现,而美国儿童表现出更好的物体控制技能。在另一项研究中,评估了 255 名来自香港的 4 至 6 名学龄前儿童和来自台湾的 544 名学龄前儿童的运动技能,并将他们在运动评估电池 (MABC) 上的表现与美国同龄儿童的标准化数据进行了比较。研究结果显示,来自香港、台湾和美国的正常发育儿童的 MABC 评分存在统计学上的显着差异,表明中国儿童的表现较差 ( 46)。
Cross-cultural differences in EF also exist, Schmitt et al. (47) reported that Chinese children displayed higher EF performance at the outset of preschool compared to their American counterparts. Additionally, another study examined the EF abilities of 119 Chinese and 139 American typically developing children aged 4–5 years. The assessment included tasks such as Head-Toes-Knee-Shoulders (testing EF in a behavioral task), Sentence Completion task (evaluating working memory), and Woodcock-Johnson Pair Cancellation task (measuring attentional control). The results of this study indicated that young Chinese children demonstrated superior performance in behavioral regulation and attentional control tasks when compared to their American counterparts, while the performance in working memory tasks was similar for both groups (45). Similarly when the EF of preschoolers in China (n = 109) and in the United States (n = 107), were assessed, results indicated that the Chinese preschoolers exhibited better performance than their American counterparts across all the EF tasks (48). Despite these findings among children without ASD, it is unclear whether analogous patterns are observed among children with ASD, who are known to exhibit deficits in these domains, across different cultural backgrounds.
EF 也存在跨文化差异,Schmitt 等人 ( 47) 报告说,与美国儿童相比,中国儿童在学龄前开始时表现出更高的 EF 表现。此外,另一项研究检查了 119 名中国儿童和 139 名美国 4-5 岁正常发育儿童的 EF 能力。评估包括头-脚-膝-肩(在行为任务中测试 EF)、句子完成任务(评估工作记忆)和 Woodcock-Johnson 配对取消任务(测量注意力控制)等任务。本研究结果表明,与美国儿童相比,中国幼儿在行为调节和注意力控制任务方面表现出优异的表现,而两组在工作记忆任务方面的表现相似 ( 45)。同样,当评估中国 (n = 109) 和美国 (n = 107) 学龄前儿童的 EF 时,结果表明中国学龄前儿童在所有 EF 任务中表现出优于美国学龄前儿童的表现 ( 48)。尽管在没有 ASD 的儿童中发现了这些发现,但尚不清楚在患有 ASD 的儿童中是否观察到类似的模式,众所周知,这些儿童在不同文化背景下在这些领域表现出缺陷。
The delineation of a particular motor cognitive relation has the potential to inform earlier identification and inform key intervention initiatives, especially for young children with ASD. Although there has been a surge of research on the link between motor skills and EF in children without ASD (49–51), few researchers have examined the association between motor skills and executive functioning in young children with ASD (52, 53). Specifically, few if any studies have examined the cross-cultural similarities and differences in such relationships in young children with ASD. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between parent ratings of motor skills and EF in children with ASD in the US and Taiwan to identify similarities and differences of associations between motor skills and EF among children with ASD across countries. The participants’ age range of 4–6 years and 11 months was chosen as it falls within the preschool period, which is a critical time for early intervention, particularly for children with ASD who are known to have deficits in both motor skills and EF. This age range provides a focused and homogeneous sample, minimizing the potential influence of additional factors that may come into play when children transition to elementary school settings. By concentrating on the preschool years, we aimed to capture the early developmental trajectory of motor skills and EF, as interventions during this period can significantly impact a child’s future outcomes. Using a cross-cultural sample of young children with ASD from Taiwan and the US, the present study provided important insights into cross-cultural universality and cultural variation in the links between motor skills and EF, especially in the autism community. Because there are few existing cross-cultural studies of the association between motor skills and EF, especially no studies in ASD children, the specific hypotheses regarding cross-cultural similarities and differences were developed based on the broader literature, including cross-cultural studies on children without ASD. It was hypothesized that (1) there would be significant associations between parent ratings of motor skills and EF in children with ASD from Taiwan and the US, respectively, and (2) the relationship between parent ratings of motor skills and EF in children with ASD from Taiwan would be stronger than the US.
特定运动认知关系的描述有可能为早期识别提供信息并为关键干预计划提供信息,尤其是对于患有 ASD 的幼儿。尽管关于无 ASD 儿童运动技能与 EF 之间联系的研究激增 ( 49-51),但很少有研究人员研究 ASD 幼儿运动技能与执行功能之间的关联 ( 52, 53)。具体来说,很少有研究(如果有的话)检查了患有 ASD 的幼儿这种关系的跨文化相似性和差异性。因此,本研究的目的是检查美国和台湾 ASD 儿童父母运动技能评分与 EF 之间的关系,以确定各国 ASD 儿童运动技能与 EF 之间关联的异同。选择参与者的年龄范围为 4-6 岁零 11 个月,因为它属于学龄前阶段,这是早期干预的关键时期,特别是对于已知在运动技能和 EF 方面都有缺陷的 ASD 儿童。这个年龄范围提供了一个集中和同质的样本,最大限度地减少了当儿童过渡到小学环境时可能起作用的其他因素的潜在影响。通过专注于学龄前阶段,我们旨在捕捉运动技能和 EF 的早期发展轨迹,因为在此期间的干预会显着影响儿童的未来结果。本研究使用来自台湾和美国的 ASD 幼儿的跨文化样本,为运动技能与 EF 之间联系的跨文化普遍性和文化差异提供了重要见解,尤其是在自闭症社区。 由于现有的关于运动技能与 EF 之间关联的跨文化研究很少,尤其是没有针对 ASD 儿童的研究,因此基于更广泛的文献开发了关于跨文化相似性和差异性的具体假设,包括对无 ASD 儿童的跨文化研究。据推测,( 1) 台湾和美国 ASD 儿童的父母运动技能评分和 EF 之间分别存在显着关联,以及 (2) 台湾 ASD 儿童的父母运动技能评分与 EF 之间的关系会比美国强。
Materials and methods 材料和方法
Sample 样本
One hundred and seventy-two parents/legal guardians of children with ASD were recruited from two countries, Taiwan (n = 100) and the US (n = 72). Inclusion criteria of the present study included being a parent/guardian of a child with ASD and the child’s: (1) current aged between 4–6 years and 11 months, and (2) parental report of their child having a diagnosis of ASD, Pervasive Developmental Disorder-Not Otherwise Specified (PDD-NOS), or Asperger syndrome. Several strategies were employed to recruit parents/guardians of children with ASD. First, social media was used to reach potential participants, including personal social media websites (e.g., Facebook and Instagram), websites and social media pages of ASD-organization and associations in Taiwan and the US, and through Facebook advertisements (e.g., paid based on geographic region). These identified websites were asked to share a pre-established flyer/message to their social media page, which includes a link to the study survey. Second, flyers and bulletins with a QR code of the survey link were sent to targeted programs, ASD support groups, disability organizations, and pediatric services both in Taiwan and the US. Lastly, a research panel was purchased from “Centiment” due to the difficulty in recruiting enough US samples.1 Centiment was chosen because of their reputation and experience in surveying respondents that are difficult to reach, and Centiment has been used in previous studies (54, 55). Statistical analyses were conducted to compare the differences between the panel sample and the other US sample. Results showed no statistically significant differences in demographic information (e.g., child age, gender, race, body mass index (BMI), whether children received physical activity or cognitive training, parental education level) and outcome variables (e.g., total motor score, fine motor skills, gross motor skills, total EF score, working memory, and inhibition). Therefore, the two US samples were combined for further analyses.
从台湾 (n = 100) 和美国 (n = 72) 两个国家招募了 172 名 ASD 儿童的父母/法定监护人。本研究的纳入标准包括成为 ASD 儿童的父母/监护人,并且孩子的:(1) 目前年龄在 4-6 岁至 11 个月之间,以及 (2) 父母报告他们的孩子被诊断为 ASD、广泛性发育障碍-未另行指定 (PDD-NOS),或阿斯伯格综合症。采用了几种策略来招募 ASD 儿童的父母/监护人。首先,社交媒体被用来接触潜在的参与者,包括个人社交媒体网站(例如 Facebook 和 Instagram)、台湾和美国的 ASD 组织和协会的网站和社交媒体页面,以及通过 Facebook 广告(例如,根据地理区域付费)。这些被识别的网站被要求将预先建立的传单/消息分享到他们的社交媒体页面,其中包括指向研究调查的链接。其次,将带有调查链接二维码的传单和公告发送给台湾和美国的目标项目、ASD 支持团体、残疾组织和儿科服务。最后,由于难以招募到足够的美国样本,从 “Centiment” 购买了一个研究小组。 1 选择 Centiment 是因为他们在调查难以接触的受访者方面的声誉和经验,并且 Centiment 已在以前的研究中使用 ( 54, 55)。进行统计分析以比较面板样本与其他美国样本之间的差异。 结果显示,人口统计信息(例如,儿童年龄、性别、种族、体重指数 (BMI)、儿童是否接受体育活动或认知训练、父母教育水平)和结果变量(例如,总运动评分、精细运动技能、粗大运动技能、EF 总分、工作记忆和抑制)没有统计学意义差异。因此,将两个美国样品合并进行进一步分析。
Measures 措施
A comprehensive online survey distributed through the Qualtrics survey system (Provo, UT; https://www.qualtrics.com) was utilized in the present study and included three sections: (a) demographic information, (b) child motor skills, and (c) child EF. The English version of the survey was used by the American participants, and the Chinese version was used for participants in Taiwan.
本研究使用通过 Qualtrics 调查系统(犹他州普罗沃;https://www.qualtrics.com)分发的综合在线调查,包括三个部分:(a) 人口统计信息,(b) 儿童运动技能,和 (c) 儿童 EF。美国参与者使用英文版调查,台湾参与者使用中文版调查。
Demographic questionnaire
人口统计问卷
A demographic questionnaire was filled out by the parent/legal guardian of the child with ASD. The questions included participant and family background information, such as child age, gender, race/ethnicity, height, and weight, whether they received physical activity (e.g., after school physical activity program, soccer, or Taekwondo) and cognitive interventions or programs (e.g., physical therapy or occupational therapy), parent/guardian age, gender, race/ethnicity, living in urban/rural area, educational level, and annual income.
ASD 儿童的父母/法定监护人填写了一份人口统计问卷。问题包括参与者和家庭背景信息,例如儿童年龄、性别、种族/民族、身高和体重,他们是否接受过体育活动(例如,课后体育活动计划、足球或跆拳道)和认知干预或计划(例如,物理治疗或职业治疗),父母/监护人年龄、性别、种族/民族、生活在城市/农村地区、教育水平、 和年收入。
Motor skill questionnaire
运动技能问卷
The motor skills were measured by the subitems of the Children Activity Scale – Parents (ChAS-P) in this study. ChAS-P is an efficient and appropriate parent-proxy questionnaire measuring the gross and fine motor skills and activities of daily living of children aged 4–8 years during everyday functional/play skills in a natural environment (56). The time for parents/guardians to complete ChAS-P is about 5 min. The questionnaire asks parents to evaluate their child’s motor skills or activity of daily living by comparing their child’s performance to another child. ChAS-P consists of 27 questions with a 5-point Likert scale ranging from 5 = “less adequately,” 4 = “adequately,” 3 = “almost well,” 2 = “well,” and 1 = “very well.” These 27 questions are grouped into four factors: gross motor skills (e.g., maintaining balance, playing in the playground), fine motor skills (e.g., writing/copying shapes, drawing), organization in space and time (representing the ability to organize movement in time and space, e.g., organizing self in preparation for going out), and activities of daily living (e.g., eating without getting dirty, self-dressing). Scores are summed for a total score ranging from 27 (lowest) to 135 (highest), with lower scores rated by parents reflecting better motor skills among children. Given the aims of the current study, fine motor skills (6 items) and gross motor skills (6 items) were used for the analyses of this study. The summary scores from motor skill subitems range from 12 (lowest) to 60 (highest).
在本研究中,运动技能由儿童活动量表 - 父母 (ChAS-P) 的子项目测量。ChAS-P 是一种有效且适当的家长代理问卷,用于测量 4-8 岁儿童在自然环境中日常功能/游戏技能中的粗大和精细运动技能以及日常生活活动 ( 56)。父母/监护人完成 ChAS-P 的时间约为 5 分钟。该问卷要求父母通过将孩子的表现与其他孩子进行比较来评估孩子的运动技能或日常生活活动。ChAS-P 由 27 个问题组成,采用 5 点李克特量表,范围从 5 =“不太充分”、4 =“充分”、3 =“几乎很好”、2 =“好”和 1 =“非常好”。这 27 个问题分为四个因素:粗大运动技能(例如,保持平衡、在场上玩耍)、精细运动技能(例如,书写/复制形状、绘画)、空间和时间组织(代表在时间和空间中组织运动的能力,例如,组织自我以准备外出)和日常生活活动(例如,吃东西不弄脏, 自我穿衣)。分数相加得出总分,从 27(最低)到 135(最高)不等,父母评分较低的分数反映儿童的运动技能较好。鉴于当前研究的目的,精细运动技能(6 项)和粗大运动技能(6 项)用于本研究的分析。运动技能子项目的总分范围从 12(最低)到 60(最高)。
The ChAS-P was selected for use because it has demonstrated good internal consistency, construct validity, and concurrent validity, with a significant moderate correlation between the Movement Assessment Battery (MABC) and ChAS-P (r = 0.51, p < 0.001) (56); in addition this assessment was free for use. Further, the ChAS-P has been used for measuring the motor performance of children with other developmental disorders, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) (57) and developmental coordination disorder (DCD) (58), and was recommended by Bardid et al. (59) as an appropriate parent proxy for measurement of motor skills when direct individually administered measures are not feasible. The author translated English version of ChAS-P to Chinese version based on the cross-cultural adaptation of instruments.
选择 ChAS-P 是因为它表现出良好的内部一致性、结构效度和并发效度,运动评估电池 (MABC) 和 ChAS-P 之间存在显著的中等相关性 (r = 0.51,p < 0.001) ( 56);此外,此评估可免费使用。此外,ChAS-P 已用于测量患有其他发育障碍的儿童的运动表现,例如注意力缺陷/多动障碍 (ADHD) ( 57) 和发育协调障碍 (DCD) ( 58),并被 Bardid 等人 ( 59) 推荐为适当的父母代理,当直接单独管理的措施不可行时,用于测量运动技能。作者根据乐器的跨文化改编,将 ChAS-P 的英文版本翻译成中文版本。
Executive function questionnaire
执行功能问卷
Childhood Executive Functioning Inventory (CHEXI) was employed to measure problems with EF. The CHEXI (60) is a 24-item parent-report inventory that assesses the behavioral manifestations of EF abilities in children aged 4 to 12 years. The CHEXI is an open-access tool with multiple language versions, including Chinese.2 The administration time of CHEXI is about 5 min for parents/ guardians to complete the form. CHEXI capitalizes on observations of children in their naturalistic settings to quantify their EF impairments during participation in regular life activities. The CHEXI is comprised of 24 questions with a 5-point Likert scale ranging from 1 being “Definitely not true” to 5 being “Definitely true.” The example items for the working memory subscale include “Has difficulty with tasks or activities that involve several steps” and “Has difficulty remembering lengthy instructions.” An example item for the inhibition subscale includes “Has difficulty holding back his/her activity despite being told to do so.” Parents/ guardians will read such a statement and indicate how well that statement is true for the child. Based on the original study conducted by the creator of the CHEXI, the questionnaire items naturally clustered into two factors when administered to young children in kindergarten (60). These factors were identified as ‘working memory,’ which encompassed the working memory (11 items) and planning (4 items) subscales, and ‘inhibition,’ which included the regulation (5 items) and inhibition (6 items) subscales, according to the guidelines provided in the questionnaire’s instructions. Each question’s scores are summed for a total score ranging from 24 being the lowest to 120 being the highest, with higher scores indicating greater EF problems.
采用儿童执行功能量表 (CHEXI) 来测量 EF 问题。CHEXI ( 60) 是一个包含 24 个项目的家长报告清单,用于评估 4 至 12 岁儿童 EF 能力的行为表现。CHEXI 是一个开放获取的工具,具有多种语言版本,包括中文。 2 CHEXI 的给药时间约为 5 分钟,家长/监护人填写表格。CHEXI 利用对儿童在自然环境中的观察来量化他们在参与正常生活活动期间的 EF 障碍。CHEXI 由 24 个问题组成,采用 5 点李克特量表,范围从 1 表示“绝对不正确”到 5 表示“绝对正确”。工作记忆子量表的示例项目包括“难以完成涉及多个步骤的任务或活动”和“难以记住冗长的说明”。抑制分量表的示例项目包括“尽管被告知仍难以抑制他/她的活动”。父母/监护人将阅读此类声明并表明该声明对孩子的真实程度。根据 CHEXI 创建者进行的原始研究,当对幼儿园的幼儿进行时,问卷项目自然地分为两个因素 ( 60)。根据问卷说明中提供的指南,这些因素被确定为“工作记忆”,包括工作记忆(11 项)和规划(4 项)分量表,以及“抑制”,包括调节(5 项)和抑制(6 项)分量表。每个问题的分数相加得到总分,从 24 分(最低)到 120 分(最高)不等,分数越高表示 EF 问题越严重。
The reason for using the CHEXI to measure EF among children with ASD was because it provides the measurement of a child’s EF deficits in the context of everyday demands as rated by parents. Research has indicated that neuropsychological tests administered in a lab may not be representative of the more complex daily lives of children (61). In addition, many lab-based EF tests have limits in their ecological validity and generalizability (62). Research also revealed that CHEXI has higher discriminant validity than the one found in neuropsychological tests (63). A recent meta-analysis study indicated that parent-reported ratings of EF had larger effect sizes compared to psychometric tests or experimental tasks (23). Thorell & Nyberg (60) suggested that questionnaires reported by raters capture the child’s behavior in the real world based on observations during an extended period. Also, evidence has shown that both English and Chinese version of CHEXI demonstrated good validity and reliability (64, 65). Further, CHEXI has been used in children with developmental disorders such as ADHD (63), and in typically developing young Taiwanese children (65).
使用 CHEXI 测量 ASD 儿童 EF 的原因是,它可以在父母评估的日常需求背景下测量儿童的 EF 缺陷。研究表明,在实验室进行的神经心理学测试可能无法代表儿童更复杂的日常生活 ( 61)。此外,许多基于实验室的 EF 测试在其生态效度和泛化性方面存在局限性 ( 62)。研究还表明,CHEXI 的判别效度高于神经心理学测试中的 CHEXI(63)。最近的一项荟萃分析研究表明,与心理测试或实验任务相比,父母报告的 EF 评分具有更大的效应量 ( 23)。Thorell & Nyberg ( 60岁) 建议,评分者报告的问卷根据长时间的观察捕捉到孩子在现实世界中的行为。此外,有证据表明,英文和中文版本的 CHEXI 都表现出良好的有效性和可靠性 ( 64, 65)。此外,CHEXI 已用于患有发育障碍的儿童,例如 ADHD ( 63 ),以及正常发育的台湾幼儿 ( 65 )。
Procedure 程序
Ethical approval for the study was received from the Institutional Review Board at Oregon State University. In both the US and Taiwan, participants were recruited from various ASD organizations, pediatric services and schools, social media websites, and advertisements (e.g., Facebook). These identified websites were asked to post to their social media page with a link to the survey. The messages were preconstructed, minimizing the work for the organizations and maximizing consistency. The time for completing the demographic questionnaire, ChAS-P, and CHEXI is usually 5 min for each (total about 15 min). As much as possible, parents/guardians were encouraged to complete the surveys in a non-distracting environment.
该研究已获得俄勒冈州立大学机构审查委员会的伦理批准。在美国和台湾,参与者是从各种 ASD 组织、儿科服务和学校、社交媒体网站和广告(例如 Facebook)中招募的。这些被识别的网站被要求发布到他们的社交媒体页面上,并附上调查的链接。消息是预先构建的,最大限度地减少了组织的工作量并最大限度地提高了一致性。完成人口统计问卷、ChAS-P 和 CHEXI 的时间通常为各 5 分钟(总共约 15 分钟)。鼓励家长/监护人尽可能在不分散注意力的环境中完成调查。
Statistical analysis 统计分析
Descriptive statistics, including means and standard deviations, were computed for demographic information (e.g., age, gender, race, BMI, IEP, whether children received physical activity or cognitive training, living area, parents/guardians age, parental education level, and annual household income), ChAS-P, and CHEXI scores. In this study, we collected a comprehensive set of demographic information from participants. These variables were chosen based on prior research indicating their potential influence on motor skills and EF, which are the primary outcome variables of interest.
针对人口统计信息(例如,年龄、性别、种族、BMI、IEP、儿童是否接受体育活动或认知训练、生活面积、父母/监护人年龄、父母教育水平和家庭年收入)、ChAS-P 和 CHEXI 分数计算描述性统计,包括平均值和标准差。在这项研究中,我们从参与者那里收集了一套全面的人口统计信息。这些变量是根据先前的研究表明它们对运动技能和 EF 的潜在影响而选择的,而 EF 是感兴趣的主要结果变量。
We also conducted several preliminary tests to determine the most relevant covariates prior to our main analyses. Chi-square tests of independence were conducted to assess associations between categorical demographic variables, including gender, IEP, whether children received physical activity or cognitive training, living area, parental educational level, and annual household income. Independent t-tests were performed to examine potential differences in continuous outcome variables, including age, BMI, and parents/guardians age, between participants from the two countries. In cases where statistical significance was observed, the variables were included as covariates in subsequent regression analyses. It is important to note that, even when certain variables such as age and gender did not exhibit statistical significance in the initial chi-square or t-tests, they were retained as covariates in the regression model. This decision was made based on theoretical considerations, acknowledging the possibility of their latent impact on the outcomes of interest. We recognize the importance of thorough covariate selection and have taken this into account in our analytical approach.
我们还进行了几次初步测试,以确定在主要分析之前最相关的协变量。进行独立性卡方检验以评估分类人口统计变量之间的关联,包括性别、 IEP、儿童是否接受体育活动或认知训练、生活面积、父母教育水平和家庭年收入。进行独立的 t 检验以检查来自两个国家的参与者之间连续结果变量的潜在差异,包括年龄、BMI 和父母/监护人年龄。在观察到统计显著性的情况下,变量作为协变量包含在随后的回归分析中。需要注意的是,即使某些变量(如年龄和性别)在初始卡方检验或 t 检验中没有表现出统计显著性,它们也会作为协变量保留在回归模型中。这一决定是基于理论考虑做出的,并承认它们对 INTEREST 结果的潜在影响的可能性。我们认识到全面协变量选择的重要性,并在我们的分析方法中考虑到了这一点。
The following outcomes of ChAS-P were used for analysis: (1) fine motor skills, (2) gross motor skills, and (3) total motor score. For the variables in EF, (1) working memory, (2) inhibition, and (3) total EF score in CHEXI were used for analysis. Previous research examining the associations between motor skills and EF in children with and without disabilities had mixed findings. While the majority of studies indicated that fine motor skills were associated with EF (31, 34, 66), some studies found associations between gross motor skills and EF (67–69). Due to the inconsistent findings in the previous research, our goal was to investigate the specific relationships between parent ratings of motor skills and EF in children with ASD in the United States.
ChAS-P 的以下结局用于分析:( 1) 精细运动技能,( 2) 粗大运动技能,以及 ( 3) 总运动评分。对于 EF 中的变量,使用 CHEXI 中的 ( 1) 工作记忆、 ( 2) 抑制和 ( 3) 总 EF 评分进行分析。先前研究检查了残疾和非残疾儿童运动技能与 EF 之间之间的关联,结果喜忧参半。虽然大多数研究表明精细运动技能与 EF 相关 ( 31, 34, 66),但一些研究发现粗大运动技能与 EF 之间存在关联 ( 67– 69)。由于之前研究的结果不一致,我们的目标是调查美国 ASD 儿童父母对运动技能评分与 EF 之间的具体关系。
Thus, to investigate these associations in children with ASD from Taiwan and the United States, separate hierarchical linear regressions were conducted.
因此,为了调查来自台湾和美国的 ASD 儿童的这些关联,进行了单独的分层线性回归。
In our hierarchical regression strategy, we systematically evaluated the relationship between parent ratings of motor skills and EF in children with ASD in both the United States and Taiwan. To ensure a comprehensive assessment while addressing potential multicollinearity issues, a two-block hierarchical linear regression approach was employed. In Block 1 of the regression models, we included all covariates that were deemed relevant to the analysis, including age, gender, BMI, whether children received physical activity or cognitive training, and parental education level. The criteria for variables assessed in Block 1 to be carried forward into Block 2 were based on their theoretical relevance to the analysis and their potential influence on the relationships under investigation. In Block 2 of the hierarchical regressions, we introduced one of the motor skills variables as the independent variable, and calculated separate regression analyses for: total motor skills, fine motor skills, and gross motor skills. This step was taken separately for participants from Taiwan and the United States, resulting in a total of 12 hierarchical linear regressions (six for participants from Taiwan and six for participants from the United States). Hierarchical regressions were employed to determine whether the independent variables (i.e., motor skills) accounted for a statistically significant portion of the variance in the dependent variable (i.e., EF) after accounting for all other covariates.
在我们的分层回归策略中,我们系统地评估了美国和台湾 ASD 儿童的父母运动技能评分与 EF 之间的关系。为了确保在解决潜在多重共线性问题的同时进行全面评估,采用了两块分层线性回归方法。在回归模型的第 1 块中,我们包括了所有被认为与分析相关的协变量,包括年龄、性别、BMI、儿童是否接受体育活动或认知训练以及父母的教育水平。将块 1 中评估的变量结转到块 2 的标准基于它们与分析的理论相关性及其对所调查关系的潜在影响。在分层回归的第 2 块中,我们引入了一个运动技能变量作为自变量,并计算了以下项的单独回归分析:总运动技能、精细运动技能和粗大运动技能。这一步骤分别针对来自台湾和美国的参与者进行,总共产生了 12 个分层线性回归(来自台湾的参与者有 6 个,来自美国的参与者有 6 个)。采用分层回归来确定在考虑所有其他协变量后,自变量(即运动技能)是否占因变量(即 EF)方差的统计学显着部分。
To examine whether children with ASD from Taiwan and the US showed different relationships between motor skills and EF, another hierarchical regression analysis was employed, with EF as the dependent variable. All covariates were entered in Block 1, and the total motor skills, country, and the interaction term of total motor skills x country were entered in Block 2. The purpose of this interaction term was to assess whether there were differences in the relationship between parent ratings of motor skills and EF in children with ASD from Taiwan and the United States. The ‘country’ was treated as a categorical variable, with two levels representing the two countries in our study, Taiwan and the United States. All statistical analyses were conducted using RStudio (version 3.6.1). An alpha level of.01 was used for all statistical tests. In this study, a more stringent alpha level for determining statistical significance was adapted, setting it at.01 instead of the conventional.05. This modification was to minimize the risk of Type I errors, especially in light of the 13 hierarchical linear regressions conducted as part of our analysis. By employing this adjusted alpha level, we aimed to control the familywise error rate across multiple tests.
为了检查来自台湾和美国的 ASD 儿童是否表现出运动技能和 EF 之间的不同关系,采用了另一种分层回归分析,以 EF 为因变量。所有协变量都输入在块 1 中,总运动技能、国家和总运动技能 x 国家的交互项输入在块 2 中。该交互项的目的是评估来自台湾和美国的 ASD 儿童的父母运动技能评分与 EF 之间的关系是否存在差异。“国家”被视为一个分类变量,两个水平代表我们研究中的两个国家,即台湾和美国。所有统计分析均使用 RStudio (版本 3.6.1) 进行。所有统计检验均使用 alpha 水平 .01。在这项研究中,采用了更严格的 alpha 水平来确定统计显着性,将其设置为 .01 而不是传统的 .05。这种修改是为了最大限度地降低 I 类错误的风险,特别是考虑到作为我们分析的一部分进行的 13 个分层线性回归。通过采用这个调整后的 alpha 水平,我们旨在控制多个测试的 familywise 错误率。
Results 结果
Descriptive analysis 描述性分析
Descriptive statistics for participants from Taiwan and the US are presented in Table 1, including means, standard deviations for continuous variables, and proportions for categorical variables. Statistical differences at the 5% significance level were observed in several demographic variables: (1) whether children with ASD received cognitive training. Children with ASD from Taiwan had a higher percentage compared to their peers from the US; (2) parental education level. Parents from Taiwan generally had higher degrees compared to parents from the United States; (3) BMI. Children with ASD from Taiwan had lower BMI compared to their peers from the US; (4) parents’ age. Parents from Taiwan were older than parents from the United States (see Table 1).
表 1 列出了来自中国台湾和美国的参与者的描述性统计量,包括均值、连续变量的标准差和分类变量的比例。在几个人口统计变量中观察到 5% 显着性水平的统计差异: ( 1) ASD 儿童是否接受认知训练。与来自美国的同龄人相比,来自台湾的 ASD 儿童的百分比更高;( 2) 父母教育水平。与来自美国的父母相比,台湾父母的学位通常更高;( 3) 体重指数。与来自美国的同龄人相比,来自台湾的 ASD 儿童的 BMI 较低;( 4) 父母的年龄。来自台湾的父母比来自美国的父母年长(见表 1)。
The descriptive statistics for motor skills (total motor skills scores, fine motor skills, and gross motor skills) and EF (total EF scores, working memory, and inhibition) were presented in Table 2. The focus of the analyses was not to make comparisons between countries in motor skills and EF. Instead, our aim was to identify similarities and differences across countries in terms of associations between motor skills and EF.
表 2 列出了运动技能 (总运动技能分数、精细运动技能和粗大运动技能) 和 EF (EF 总分、工作记忆和抑制)的描述性统计数据。分析的重点不是在国家之间的运动技能和 EF 进行比较。相反,我们的目标是根据运动技能和 EF 之间的关联确定各国之间的相似性和差异性。
Analytic strategy 分析策略
It is important to note that the results from the hierarchical regression analyses presented below were conducted separately for children with ASD from Taiwan and the United States to explore the relationships within each cultural context. This approach allowed us to gain insights into the associations between motor skills and EF while considering the unique characteristics within each group.
值得注意的是,下面介绍的分层回归分析的结果是分别针对来自台湾和美国的 ASD 儿童进行的,以探索每种文化背景下的关系。这种方法使我们能够深入了解运动技能和 EF 之间的关联,同时考虑每组内的独特特征。
Working memory 工作记忆
The hierarchical regression analysis indicated that Taiwanese children with ASD had parent ratings of total motor skills that were significantly related to ratings of working memory after controlling for covariates (β = 0.39, p < 0.001). Overall, the model including Taiwanese children with ASD explained nearly 28% of the variance in working memory (i.e., adjusted R2 = 0.28). American children with ASD had total motor skill ratings that were also significantly associated with ratings of working memory (β = 0.57, p < 0.001) after controlling for covariates. The model including American children with ASD accounted for nearly 31% of the variance in working memory (i.e., adjusted R2 = 0.31) (see Table 3).
分层回归分析表明,台湾 ASD 儿童的总运动技能家长评分与控制协变量后的工作记忆评分显著相关 (β = 0.39,p < 0.001)。总体而言,包括台湾 ASD 儿童的模型解释了近 28% 的工作记忆方差(即调整后的 R 2 = 0.28)。在控制协变量后,美国 ASD 儿童的总运动技能评分也与工作记忆评分 (β = 0.57,p < 0.001) 显着相关。包括美国 ASD 儿童的模型占工作记忆方差的近 31%(即调整后的 R 2 = 0.31)(见表 3)。
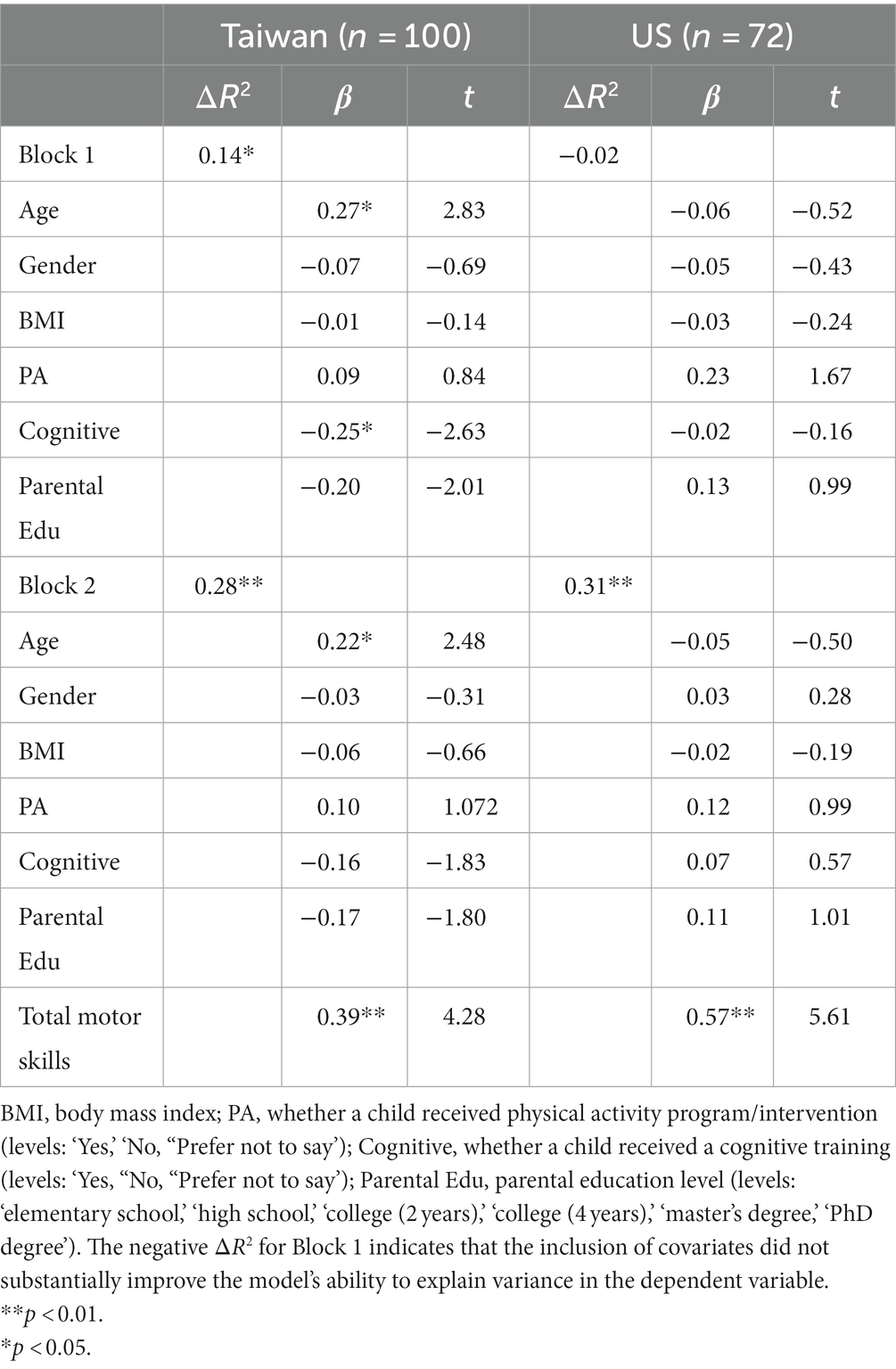
Table 3. Hierarchical multiple regression analyses for total motor skills predicting working memory.
表 3.预测工作记忆的总运动技能的分层多元回归分析。
The association between parent ratings of fine motor skills and working memory of Taiwanese children with ASD was significant in Block 2 of hierarchical regression analysis after controlling for covariates (β = 0.41, p < 0.001). Overall, the model including Taiwanese children with ASD explained nearly 29% of the variance in working memory (i.e., adjusted R2 = 0.29). In addition, the association between fine motor skills and working memory ratings of American children with ASD was also significant after accounting for covariates (β = 0.53, p < 0.001). The model including American children with ASD accounted for 24% of the variance in working memory (i.e., adjusted R2 = 0.24) as shown in Table 4.
在控制协变量后,台湾 ASD 儿童的精细运动技能父母评分与工作记忆之间的关联在分层回归分析的第 2 块中是显着的 (β = 0.41,p < 0.001)。总体而言,包括台湾 ASD 儿童的模型解释了近 29% 的工作记忆方差(即调整后的 R 2 = 0.29)。此外,在考虑协变量后,美国 ASD 儿童的精细运动技能与工作记忆评分之间的关联也很显著 (β = 0.53,p < 0.001)。如表 4 所示,包括美国 ASD 儿童的模型占工作记忆方差的 24%(即调整后的 R 2 = 0.24)。
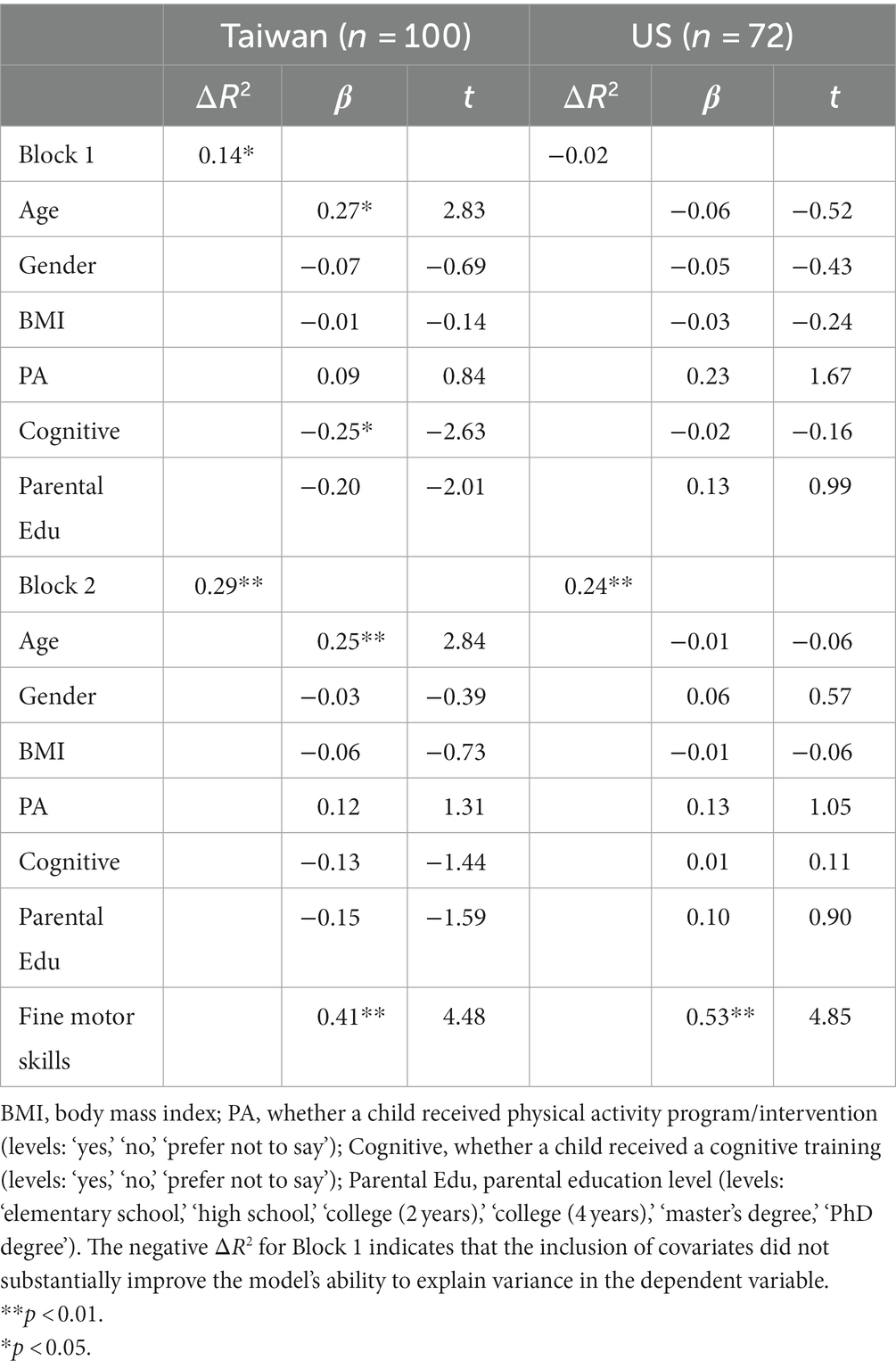
Table 4. Hierarchical multiple regression analyses for fine motor skills predicting working memory.
表 4.预测工作记忆的精细运动技能的分层多元回归分析。
After controlling for covariates, parent ratings of gross motor skills were significantly associated with working memory ratings among children with ASD from Taiwan (β = 0.26, p = 0.006). Overall, the model including Taiwanese children with ASD explained 20% of the variance in working memory (i.e., adjusted R2 = 0.20). Further, children with ASD from the US had gross motor skill ratings that were significantly related to ratings of working memory after controlling for covariates (β = 0.55, p < 0.001). The model including American children with ASD accounted for nearly 28% of the variance in working memory (i.e., adjusted R2 = 0.28) (see Table 5).
在控制协变量后,父母对粗大运动技能的评分与台湾 ASD 儿童的工作记忆评分显著相关 (β = 0.26,p = 0.006)。总体而言,包括台湾 ASD 儿童的模型解释了 20% 的工作记忆方差 (即,调整后的 R 2 = 0.20)。此外,来自美国的 ASD 儿童的粗大运动技能评级与控制协变量后的工作记忆评级显着相关 (β = 0.55,p < 0.001)。包括美国 ASD 儿童的模型占工作记忆方差的近 28%(即调整后的 R 2 = 0.28)(见表 5)。
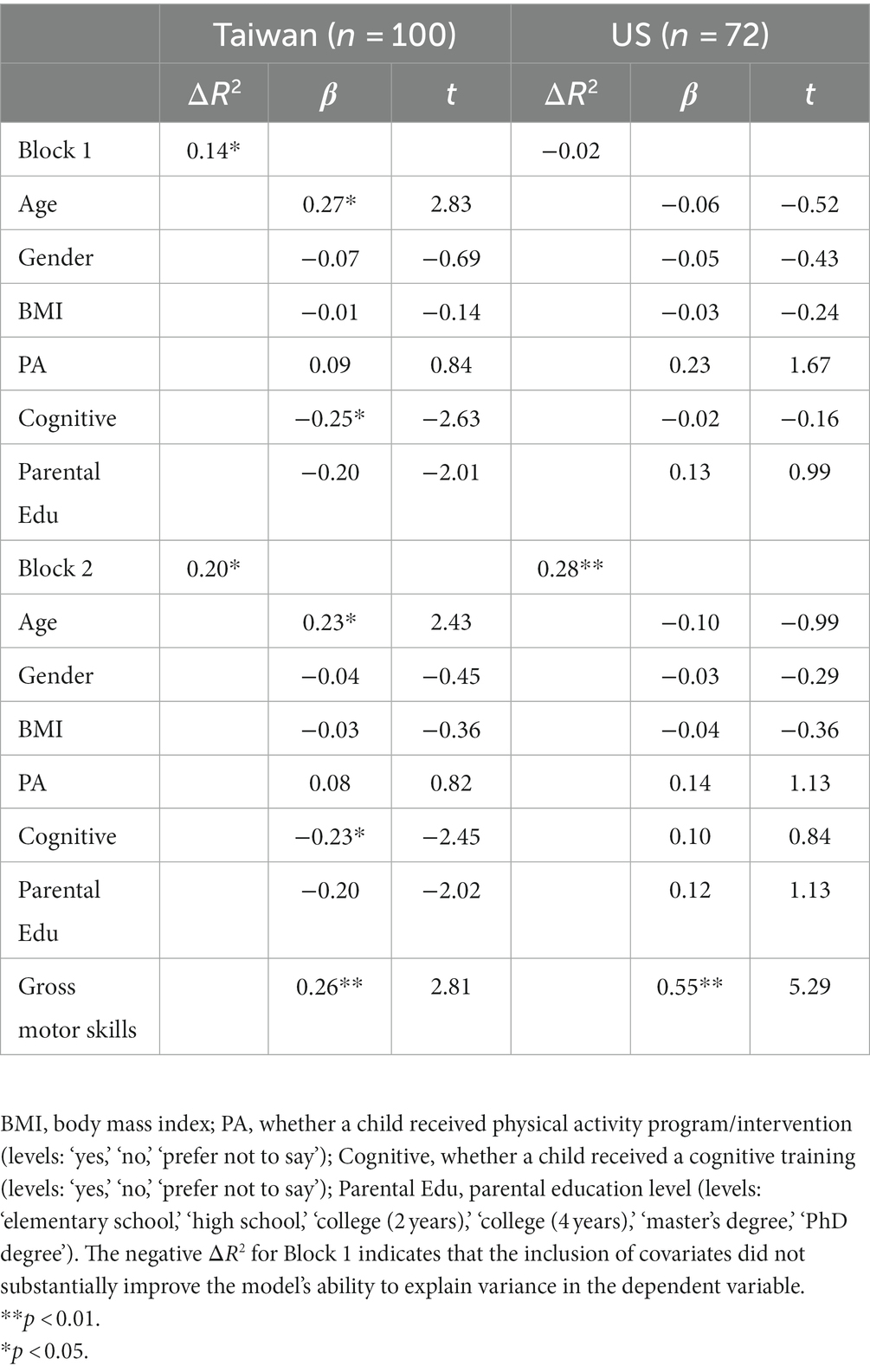
Table 5. Hierarchical multiple regression analyses for gross motor skills predicting working memory.
表 5.预测工作记忆的粗大运动技能的分层多元回归分析。
Inhibition 抑制
The hierarchical regression analysis showed that, under the more stringent alpha level of 0.01, the association between parent ratings of total motor skills and inhibition among Taiwanese children with ASD did not reach statistical significance after controlling for covariates (β = 0.26, p = 0.01). Overall, the model including children with ASD from Taiwan explained nearly 12% of the variance in inhibition (i.e., adjusted R2 = 0.12). American children with ASD had total motor skill ratings that were significantly associated with ratings of inhibition after accounting for covariates (β = 0.40, p < 0.001). The model including children with ASD from the US accounted for 14% of the variance in inhibition (i.e., adjusted R2 = 0.14), as shown in Table 6.
分层回归分析显示,在更严格的 alpha 水平 0.01 下,父母对 ASD 儿童的总运动技能评分与抑制之间的关联在控制协变量后未达到统计学意义 (β = 0.26,p = 0.01)。总体而言,包括来自台湾的 ASD 儿童的模型解释了近 12% 的抑制方差 (即,调整后的 R 2 = 0.12)。美国 ASD 儿童的总运动技能评分与考虑协变量后的抑制评分显着相关 (β = 0.40,p < 0.001)。包括来自美国的 ASD 儿童的模型占抑制方差的 14%(即调整后的 R 2 = 0.14),如表 6 所示。
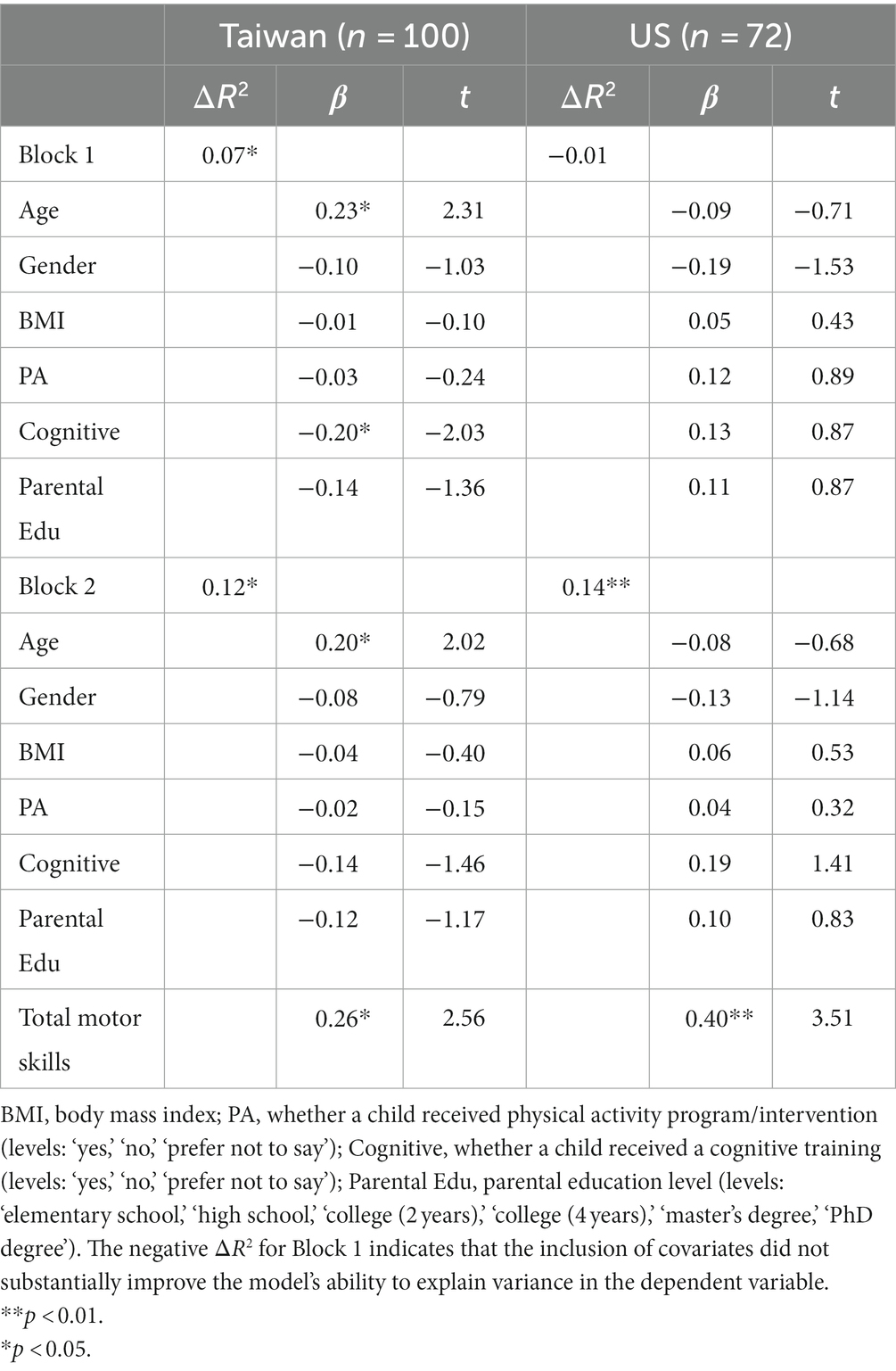
Table 6. Hierarchical multiple regression analyses for total motor skills predicting inhibition.
表 6.预测抑制的总运动技能的分层多元回归分析。
When considering the fine motor skills of Taiwanese children with ASD, the association with inhibition remained non-significant in Block 2 of hierarchical regression analysis after controlling for covariates (β = 0.21, p = 0.04) under the more stringent alpha level, accounting for approximately 10% of the variance in inhibition (i.e., adjusted R2 = 0.10). However, the association between fine motor skills and inhibition ratings of American children with ASD remained significant after accounting for covariates (β = 0.39, p = 0.001). The model including children with ASD from the US accounted for nearly 13% of the variance in working memory (i.e., adjusted R2 = 0.13) (see Table 7).
当考虑台湾 ASD 儿童的精细运动技能时,在控制协变量 (β = 0.21,p = 0.04) 后,在更严格的 alpha 水平下,分层回归分析的第 2 块中与抑制的关联仍然不显著,约占抑制方差的 10%(即,调整后的 R 2 = 0.10)。然而,在考虑协变量后,美国 ASD 儿童的精细运动技能与抑制评分之间的关联仍然显着 (β = 0.39,p = 0.001)。包括来自美国的 ASD 儿童的模型占工作记忆方差的近 13%(即调整后的 R 2 = 0.13)(见表 7)。
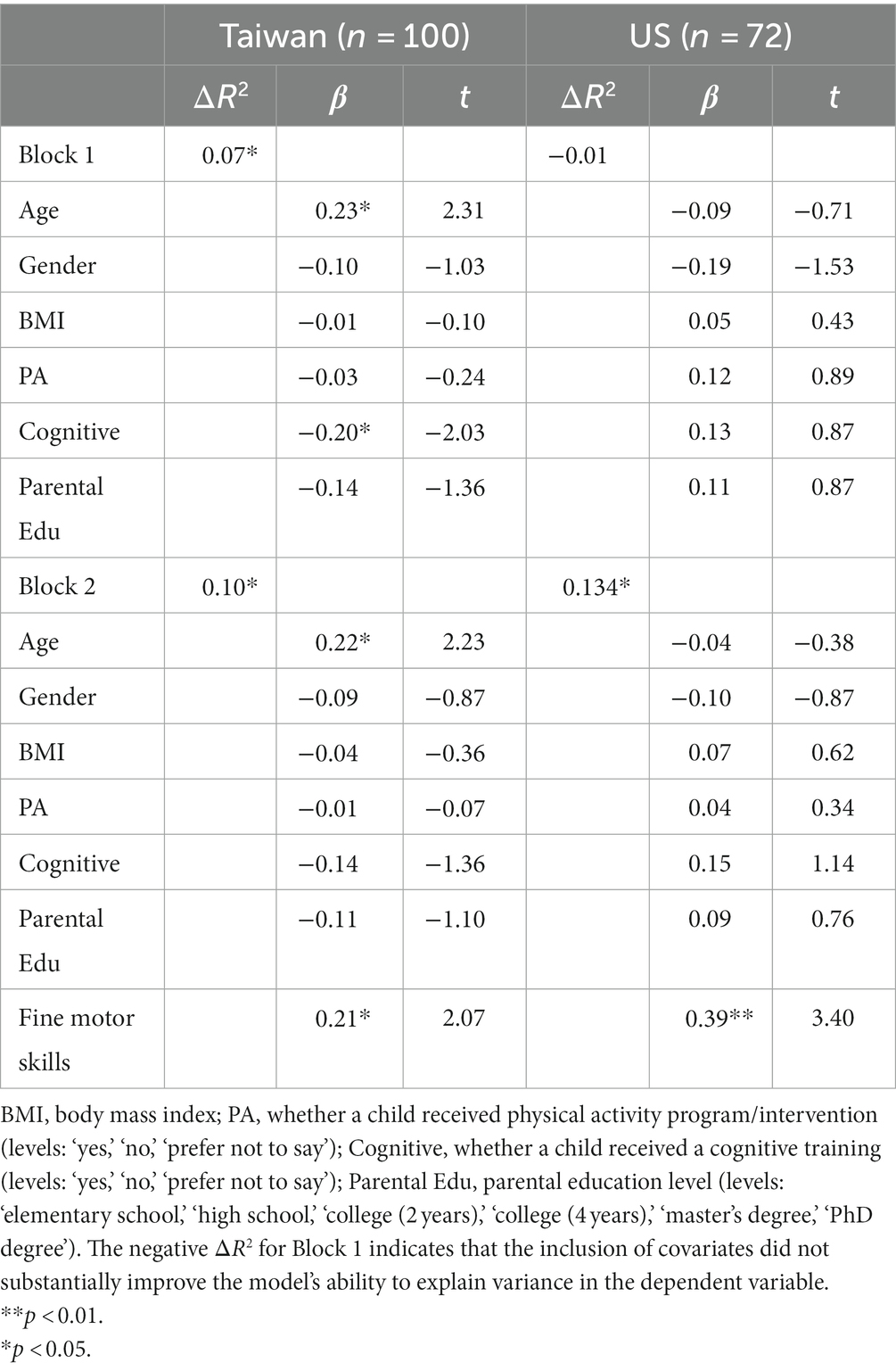
Table 7. Hierarchical multiple regression analyses for fine motor skills predicting inhibition.
表 7.精细运动技能预测抑制的分层多元回归分析。
Similarly, after applying the stricter alpha level of 0.01, the relationship between parent ratings of gross motor skills and inhibition remained non-significant for Taiwanese children with ASD after controlling for covariates (β = 0.22, p = 0.03), explaining approximately 11% of the variance in inhibition (i.e., adjusted R2 = 0.11). Nonetheless, American children with ASD had gross motor skills ratings that were significantly associated with ratings of inhibition after accounting for covariates (β = 0.35, p = 0.003). The model including children with ASD from the US accounted for nearly 11% of the variance in inhibition (i.e., adjusted R2 = 0.11) (see Table 8).
同样,在应用更严格的 alpha 水平 0.01 后,在控制协变量后,台湾 ASD 儿童的父母粗大运动技能评分与抑制之间的关系仍然不显著 (β = 0.22,p = 0.03),解释了大约 11% 的抑制方差(即,调整后的 R 2 = 0.11)。尽管如此,美国 ASD 儿童的粗大运动技能评级与考虑协变量后的抑制评级显著相关 (β = 0.35,p = 0.003)。包括来自美国的 ASD 儿童的模型占抑制方差的近 11%(即,调整后的 R 2 = 0.11)(见表 8)。
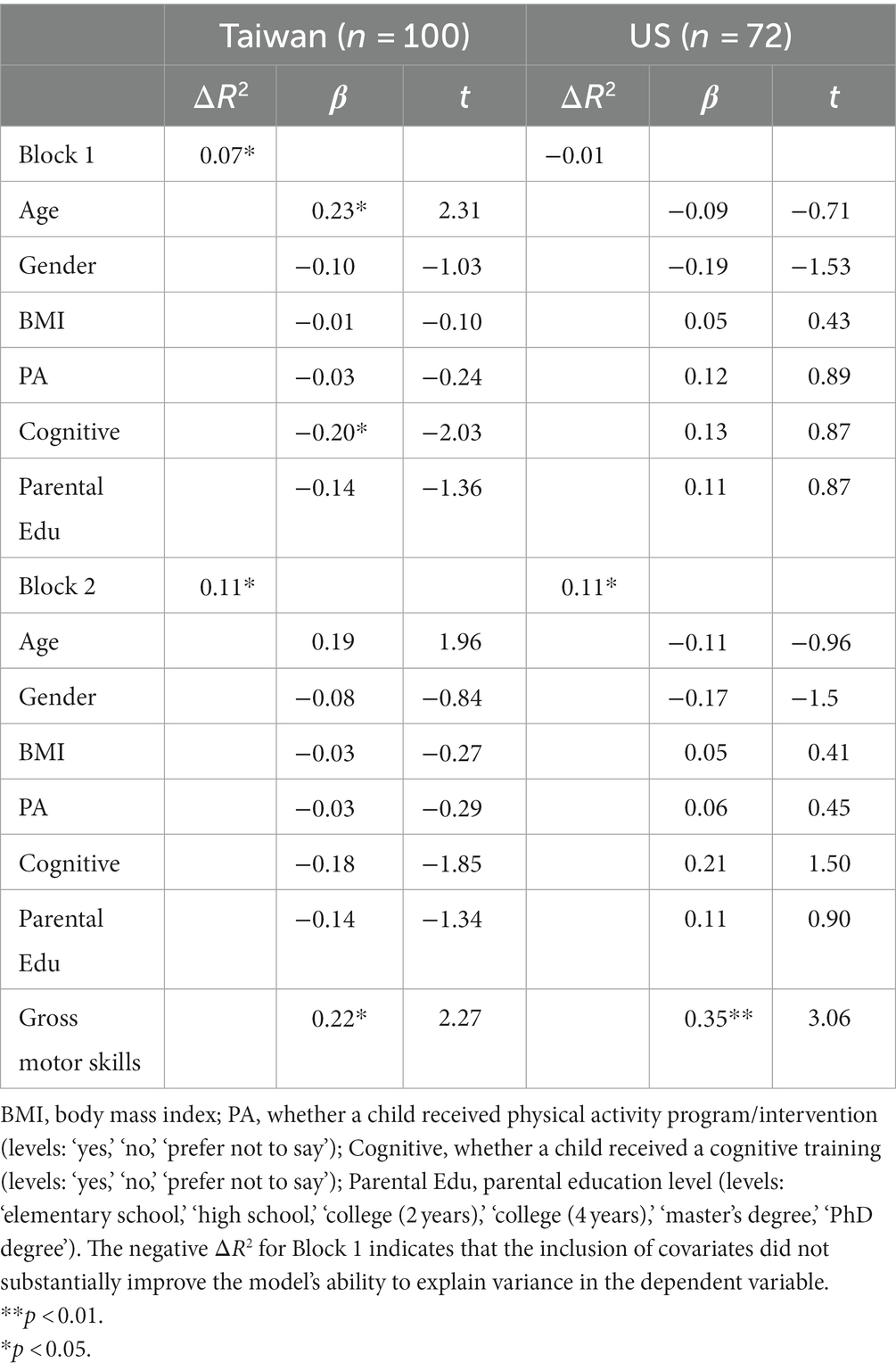
Table 8. Hierarchical multiple regression analyses for gross motor skills predicting inhibition.
表 8.预测抑制的粗大运动技能的分层多元回归分析。
The last regression model showed that the interaction term between motor skills and the country was not significant, indicating that the differences in associations between parent ratings of motor skills and EF did not vary as a function of the country (β = 0.06–0.09, p = 0.64–0.83) (see Table 9). In other words, the relation between motor skills and EF ratings was not significantly different in children with ASD from Taiwan compared to the children with ASD from the United States.
最后一个回归模型显示,运动技能与国家之间的交互项不显著,表明父母对运动技能和 EF 的相关性差异不随国家的变化而变化(β = 0.06-0.09,p = 0.64-0.83)(见表 9)。换句话说,与美国 ASD 儿童相比,台湾 ASD 儿童的运动技能和 EF 评分之间的关系没有显著差异。
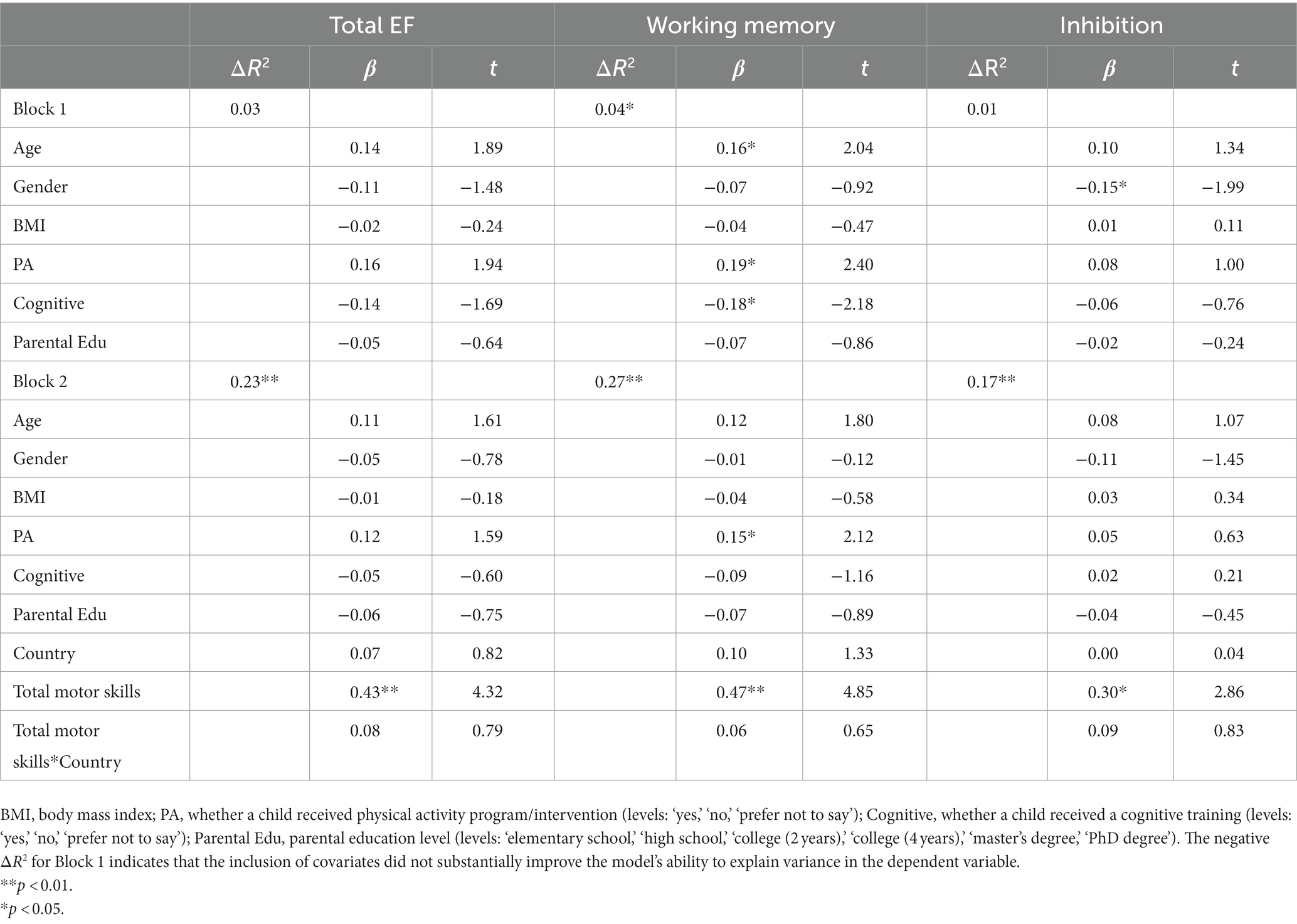
Table 9. Hierarchical multiple regression analyses for motor skills predicting EF (Combined data from Taiwan and the United States, n = 172).
表 9.预测 EF 的运动技能的分层多元回归分析(来自台湾和美国的合并数据,n = 172)。
Discussion 讨论
The purpose of this study was to examine the relationships between parent ratings of motor skills and EF in children with ASD from the United States and Taiwan. Specifically, this study aimed to answer (1) what is the relationship between motor skills and EF ratings in young children with ASD from Taiwan and the US and (2) how do such relationships in children with ASD in Taiwan differ from the children with ASD in the US? Results indicated that parent ratings of total motor skills, fine motor skills, and gross motor skills were significantly associated with EF in both working memory and inhibition in both countries. However, non-significant associations between parent-rated total motor skills, fine motor skills, and gross motor skills, and inhibition among Taiwanese children with ASD were observed under a more stringent alpha level. Another important finding was that considerable similarities were revealed between Taiwan and the US children with ASD in the relationships between ratings of motor skills and EF. This is one of the first studies, to the authors’ knowledge, investigating the associations between motor skills, including both fine and gross motor skills, and EF, including working memory and inhibition, in young children with ASD across two countries.
本研究的目的是检查来自美国和台湾的 ASD 儿童的父母运动技能评分与 EF 之间的关系。具体来说,本研究旨在回答 (1) 台湾和美国 ASD 幼儿的运动技能和 EF 评级之间有什么关系,以及 (2) 台湾 ASD 儿童的这种关系与美国的 ASD 儿童有何不同?结果表明,在这两个国家,父母对总运动技能、精细运动技能和粗大运动技能的评分与工作记忆和抑制的 EF 显著相关。然而,在更严格的 alpha 水平下,观察到父母评定的总运动技能、精细运动技能和粗大运动技能与台湾 ASD 儿童的抑制之间存在不显著的关联。另一个重要的发现是,台湾和美国的 ASD 儿童在运动技能评分与 EF 之间的关系方面显示出相当大的相似性。据作者所知,这是最早的研究之一,调查了两个国家 ASD 幼儿的运动技能(包括精细和粗大运动技能)与 EF(包括工作记忆和抑制)之间的关联。
Findings indicated that the significant associations between ratings of motor skills and EF in children with ASD did not depend on country, suggesting that these relationships are culturally comparable, with significant and positive correlations of magnitude in both countries. No research, to date, has explored the link between motor skills and EF in young children with ASD cross-culturally. It might be possible that the relation between motor skills and EF follow the same developmental timeframe and trajectory, regardless of the different contextual influences, such as geographical, cultural, and educational factors. While the exploratory nature of this study warrants future cross-cultural research, the current findings partially corroborate evidence from previous research on children with ASD in western countries (36, 52, 70). Schurink et al. (36) found significant relationships between manual dexterity, balance, and planning ability measured by objective assessments among children with PDD-NOS, a type of ASD, indicating that inferior motor skills performance is associated with poorer EF. Such a relationship may be explained by considering that substantial comorbidity between deficits in motor skills and cognitive functioning was observed in children with neurodevelopmental disorders. Indeed, several studies have suggested that the relations between motor skills and cognitive development were manifested in children with intellectual disabilities (71–73), Down syndrome (74), developmental coordination disorder (75) and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (76). Recently, one study utilized objective assessments to examine the relationship between EF, particularly attention and impulse control, and motor function in 15 school-aged children with ASD aged 8–14 years in the US. The findings revealed significant associations between EF and motor functions in children with ASD (77). In addition, Kim and colleagues (52) identified that fine motor skills, as opposed to gross motor skills, were predictive of cognitive skill enhancements after adjusting for demographic variables and initial skill levels in a cohort of pre-kindergarten American children with developmental disabilities, including those with ASD. It’s crucial to note the methodological differences between these studies and the present research. While the aforementioned studies relied on objective assessments, our study utilized subjective parent reports. Additionally, the age range of participants in our study is different from the studies above. As a result, when interpreting the findings and considering their implications, it is important to exercise caution and take into account these variations. Although the adoption of a stricter alpha level (i.e., 0.001) led to the non-significance of certain correlations between motor skills and EF in our study, it is noteworthy that the effect sizes of our findings remain consistent with those observed in the studies mentioned earlier (52, 77), demonstrating moderate relationships between motor skills and EF among children with ASD. Thus, the present study contributes to a greater magnitude of existing literature in the field of disability, indicating the relationship between motor skills and two domains of EF (i.e., working memory and inhibition) among young children with ASD from different countries.
研究结果表明,ASD 儿童运动技能评分与 EF 之间的显着关联并不取决于国家,这表明这些关系在文化上具有可比性,在两个国家具有显着和正相关的幅度。迄今为止,还没有研究探讨跨文化 ASD 幼儿运动技能与 EF 之间的联系。运动技能和 EF 之间的关系可能遵循相同的发展时间框架和轨迹,而不管不同的环境影响,例如地理、文化和教育因素。虽然这项研究的探索性值得未来的跨文化研究,但目前的发现部分证实了先前对西方国家 ASD 儿童的研究证据 ( 36, 52, 70)。Schurink 等人 ( 36) 发现,通过客观评估测量 PDD-NOS(一种 ASD)儿童的手部灵活性、平衡和规划能力之间存在显着关系,这表明较差的运动技能表现与较差的 EF 相关。这种关系可以通过考虑在神经发育障碍儿童中观察到运动技能和认知功能缺陷之间的大量共病来解释。事实上,几项研究表明,运动技能和认知发展之间的关系在智障 (71-73)、唐氏综合症 (74)、发育协调障碍 (75) 和注意力缺陷多动障碍 (76) 的儿童中表现出来。 最近,一项研究利用客观评估来检查美国 15 名 8-14 岁 ASD 学龄儿童的 EF(特别是注意力和冲动控制)与运动功能之间的关系。研究结果揭示了 EF 与 ASD 儿童运动功能之间的显着关联 ( 77)。此外,Kim 及其同事 ( 52) 发现,在调整了一组患有发育障碍的美国学前儿童(包括 ASD 儿童)的人口统计变量和初始技能水平后,精细运动技能(与粗大运动技能相反)可以预测认知技能的增强。重要的是要注意这些研究和当前研究之间的方法差异。虽然上述研究依赖于客观评估,但我们的研究使用了主观的家长报告。此外,我们研究中参与者的年龄范围与上述研究不同。因此,在解释调查结果并考虑其影响时,重要的是要谨慎行事并考虑这些变化。尽管采用更严格的 alpha 水平(即 0.001)导致在我们的研究中运动技能和 EF 之间的某些相关性不重要,但值得注意的是,我们研究结果的效应大小与前面提到的研究中观察到的一致 (52, 77),表明 ASD 儿童的运动技能和 EF 之间存在中等关系。因此,本研究有助于残疾领域更广泛的现有文献,表明来自不同国家的 ASD 幼儿的运动技能与 EF 的两个领域(即工作记忆和抑制)之间的关系。
The current findings are in accordance with the theoretical framework of learning to learn (40) and embodied cognition theory (39), which suggests that cognition develops as a result of an agent’s bodily interactions with their surroundings. For instance, children develop the capacity for problem-solving through the interaction of their motor behavior and exploring and interacting with the environment. With this, early motor skills seem to lay the foundation for later cognitive development among children. The theoretical perspective was further supported by neuroimaging research (41). Empirical evidence has revealed that the rostral premotor cortex connects between motor and cognitive networks and that brain regions previously thought to be involved only in motor activities (i.e., cerebellum and basal ganglia) or cognitive activities (i.e., the prefrontal cortex) are co-activating while people engage in certain cognitive and motor tasks. (41, 78). Moreover, previous evidence has revealed that motor and cognitive development are highly associated and further suggested that motor behaviors that facilitate interaction with the environment during early childhood are critical for cognitive growth (79). Our findings further reinforce the theorized and neuroimaging evidence on the associations between motor skills and EF in the ASD population.
目前的发现符合学习的理论框架 ( 40) 和具身认知理论 ( 39),这表明认知是主体与周围环境的身体互动的结果。例如,儿童通过运动行为的互动以及探索和与环境互动来培养解决问题的能力。因此,早期运动技能似乎为儿童以后的认知发展奠定了基础。神经影像学研究进一步支持了理论观点 ( 41)。经验证据表明,喙前运动皮层连接运动和认知网络,以前被认为只参与运动活动(即小脑和基底神经节)或认知活动(即前额叶皮层)的大脑区域在人们从事某些认知和运动任务时正在共同激活。( 41, 78).此外,先前的证据表明,运动和认知发展高度相关,并进一步表明,促进儿童早期与环境互动的运动行为对认知成长至关重要 ( 79)。我们的研究结果进一步加强了 ASD 人群运动技能与 EF 之间关联的理论和神经影像学证据。
Motor skills and working memory
运动技能和工作记忆
Consistent with our hypothesis, the findings of the present study showed that both parent ratings of fine and gross motor skills were significantly related to working memory ratings in children with ASD from Taiwan and the US. Our results corroborate previous studies revealing that fine motor skills are associated with working memory in children at-risk/with ASD (80, 81) and preschool-aged children without ASD (72). Rosenblum et al. (80) suggested a significant relationship between handwriting and working memory among school-aged children with ASD. Authors assumed that handwriting, especially in the context of story-writing, might be difficult and particularly affected by even minor distractions for children with ASD, who are known to have deficits in working memory. Another plausible explanation might be the fact that working memory is needed for various activities involving fine motor skills, especially visual-motor integration (33). The items evaluating fine motor skills in the current study consisted of how well a child does in using scissors for cutting, in the constructive play and creative activities (e.g., Lego). These complex motor tasks, such as building blocks or manipulating scissors to cut along a line, likely involve the processes of working memory to control the coordination necessary to complete the activity/task successfully (34). Indeed, children spend a significant amount of time engaged in fine motor skills such as drawing, cutting, folding, and manipulating objects in preschool settings (82, 83). These activities have certain demand on fine motor skills and visuomotor integration, which are necessary for executive functioning, including working memory among young children.
与我们的假设一致,本研究的结果表明,来自台湾和美国的 ASD 儿童的父母精细和粗大运动技能评分都与工作记忆评分显着相关。我们的结果证实了以前的研究,揭示了精细运动技能与高危/患有 ASD 的儿童 ( 80, 81) 和没有 ASD 的学龄前儿童 ( 72) 的工作记忆相关。Rosenblum 等人 ( 80) 表明,在 ASD 学龄儿童中,笔迹和工作记忆之间存在显着关系。作者假设笔迹,尤其是在写故事的背景下,可能会很困难,并且特别会受到 ASD 儿童的哪怕是轻微的干扰的影响,因为众所周知,ASD 儿童有工作记忆缺陷。另一个合理的解释可能是,涉及精细运动技能的各种活动都需要工作记忆,尤其是视觉运动整合 ( 33)。在当前研究中,评估精细运动技能的项目包括儿童使用剪刀剪发、建设性游戏和创造性活动(例如乐高)的表现。这些复杂的运动任务,例如积木或纵剪刀沿一条线切割,可能涉及工作记忆的过程,以控制成功完成活动/任务所需的协调 ( 34)。事实上,在学龄前环境中,孩子们花费大量时间从事精细运动技能,例如绘画、切割、折叠和作物体 ( 82, 83)。这些活动对精细运动技能和视觉运动整合有一定的要求,这些都是执行功能所必需的,包括幼儿的工作记忆。
In line with previous studies in typically developing children (84–86) and children with intellectual disabilities (71), our findings showed that gross motor skills ratings are associated with ratings of working memory in young children with ASD. While speculative in nature, a possible explanation for such findings might be the underlying cerebellar processes. The lateral zone of the cerebellum is intricately involved in regulating the motor activity of the whole body, namely the gross motor skills (87). Neuroimaging research has indicated the activation of the cerebellum during working memory tasks (88). Collectively, the present study differs from earlier research on children with ASD by offering a more nuanced understanding of the associations between fine and gross motor skills and working memory in both western and eastern countries.
与之前对正常发育儿童 (84-86) 和智障儿童 (71) 的研究一致,我们的研究结果表明,粗大运动技能评级与 ASD 幼儿的工作记忆评级相关。虽然本质上是推测性的,但对此类发现的可能解释可能是潜在的小脑过程。小脑的外侧区错综复杂地参与调节全身的运动活动,即粗大运动技能 ( 87)。神经影像学研究表明,在工作记忆任务期间小脑会激活 ( 88)。总的来说,本研究与早期对 ASD 儿童的研究不同,它对东西方国家的精细和粗大运动技能与工作记忆之间的关联提供了更细致的理解。
Motor skills and inhibition
运动技能和抑制
The findings of this study indicated a significant association between parent ratings of fine and gross motor skills and inhibition ratings in children with ASD from the US. However, this association was not observed as significant among the Taiwanese children with ASD when adopting a stricter alpha level. This result mimics previous research on young children without ASD (49). Livesey et al. (49) utilized objective motor skill assessment (i.e., MABC) and Stroop test and indicated a significant association between motor skills and inhibitory control among 5–6 years old children without ASD. In addition to the explanation of co-activation of brain areas, this association between motor skills and inhibition might be posited from a behavioral learning perspective (89). For example, when children with ASD are in a learning environment, such as in preschool settings, they must pay attention and inhibit unrelated behaviors to properly demonstrate a fine motor task, such as writing, stringing beads, and manipulating objects. Inhibition is especially critical for young children, who may be more susceptible to environmental distractions in their surroundings. Evidence has suggested that inhibition emerges first during development in order for young children to ignore irrelevant stimuli and solve the problem (90). The ability to inhibit pre-potent responses might be an important first step in learning among young children.
这项研究的结果表明,父母对美国 ASD 儿童的精细和粗大运动技能评分与抑制评分之间存在显着关联。然而,当采用更严格的 alpha 水平时,在患有 ASD 的台湾儿童中未观察到这种关联显着。这一结果模仿了以前对没有 ASD 的幼儿的研究 ( 49)。Livesey 等人 ( 49) 利用客观运动技能评估(即 MABC)和 Stroop 测试,表明 5-6 岁无 ASD 儿童的运动技能与抑制控制之间存在显着关联。除了解释大脑区域共同激活之外,运动技能和抑制之间的这种关联也可以从行为学习的角度提出 ( 89)。例如,当 ASD 儿童处于学习环境中时,例如在学前环境中,他们必须注意并抑制不相关的行为,以正确展示精细运动任务,例如书写、串珠和作物体。抑制对幼儿尤其重要,他们可能更容易受到周围环境干扰的影响。有证据表明,抑制首先出现在发育过程中,以便幼儿忽略不相关的刺激并解决问题 ( 90)。抑制有效反应的能力可能是幼儿学习的重要第一步。
While gross motor skills are generally considered to be associated with social skills or physical well-being (91), our results revealed that children with ASD’s gross motor skills ratings were significantly related to ratings of inhibition. This finding is consistent with previous cross-sectional (49) and longitudinal research (69). Wu et al. (69) have indicated that the early gross motor ability of 2-year-old infants predicts their inhibitory control at 3 years. In addition, evidence has suggested that the motor planning ability among children was associated with the capacity to inhibit a potent but irrelevant response (92). The item measured gross motor skills in ChAS-P included not only movement skills and ball skills but also included the item of maintaining balance while performing various activities (i.e., moving through obstacle courses), which likely involves certain aspects of motor planning. Further, this finding is aligned with the results of physical activity intervention studies. Research has revealed that physical activity involving gross motor exercise positively facilitates the processes of inhibitory control (93, 94). Our results highlight the importance of engaging in gross motor opportunities for children with ASD, given its association with inhibition.
虽然粗大运动技能通常被认为与社交技能或身体健康相关 ( 91),但我们的结果显示,患有 ASD 的儿童的大运动技能评级与抑制评级显着相关。这一发现与之前的横断面研究 ( 49) 和纵向研究 ( 69) 一致。Wu 等人 ( 69) 指出,2 岁婴儿的早期粗大运动能力预示着他们在 3 岁时的抑制控制。此外,有证据表明,儿童的运动规划能力与抑制有效但不相关的反应的能力有关 ( 92)。在 ChAS-P 中测量粗大运动技能的项目不仅包括运动技能和球技能,还包括在进行各种活动(即穿越障碍课程)时保持平衡的项目,这可能涉及运动规划的某些方面。此外,这一发现与身体活动干预研究的结果一致。研究表明,涉及粗大运动运动的体育活动对抑制控制过程有积极促进 (93, 94)。鉴于 ASD 与抑制的关联,我们的结果强调了参与 ASD 儿童粗大运动机会的重要性。
The findings of the present study also revealed that ratings of fine motor skills had higher associations with EF ratings than gross motor skills. This result is aligned with research on children without ASD (95) as well as children with disabilities (72, 73). The difference observed in the link between gross motor skills and fine motor skills with EF may be attributable to the fact that fine motor skills exert a greater demand on the integrity of the cortical nervous system, specifically the frontoparietal network (96). Additionally, while the relationships between parent ratings of motor skills and EF were not significantly different in children with ASD from Taiwan and the US, the lower standardized beta coefficients were observed in Taiwanese children. This finding might be partially due to other influences of contextual factors. Evidence has indicated that both personal (e.g., comorbidity) and environmental factors (e.g., parenting practice) might affect motor and cognitive development (32, 97). However, information such as ADHD symptoms or parenting style is unavailable in this study. Thus, it is essential to acknowledge the influence of these factors on the association between ratings of motor skills and EF among young children with ASD.
本研究的结果还显示,精细运动技能评级与 EF 评级的相关性高于粗大运动技能。这一结果与对无 ASD 儿童 ( 95) 和残疾儿童 ( 72, 73) 的研究一致。在 EF 的粗大运动技能和精细运动技能之间的联系中观察到的差异可能归因于以下事实:精细运动技能对皮质神经系统的完整性有更大的要求,特别是额顶叶网络 ( 96)。此外,虽然来自台湾和美国的 ASD 儿童的父母运动技能评分与 EF 之间的关系没有显著差异,但在台湾儿童中观察到较低的标准化 beta 系数。这一发现可能部分是由于环境因素的其他影响。有证据表明,个人因素(例如,合并症)和环境因素(例如,育儿实践)都可能影响运动和认知发展 ( 32, 97)。但是,本研究中没有 ADHD 症状或养育方式等信息。因此,必须承认这些因素对 ASD 幼儿运动技能评级与 EF 之间关联的影响。
Children with ASD often experience deficits in various domains that have long-term consequences. Motor skills difficulty puts an additional burden on the child and could impact their health, daily life, and social interactions considerably. Therefore, assessing and knowing the roles of fine and gross motor skills might help parents and professionals identify skills and programs that can be intervened early on in improvements of EF, which might also help provide these young children with ASD to reach their full potential in their developmental trajectory. The present findings provide some critical practical implications for parents and practitioners working with young children with ASD. Parents and practitioners should be aware of the specific relationship between both motor skills (i.e., fine and gross motor skills) and EF (i.e., working memory and inhibition). Such specific associations might indicate that early measurement of motor skills may be particularly beneficial for a child’s higher-order cognitive development, given the observed links between motor skills and EF. Neuroimaging evidence has indicated that the areas of the brain linked with more basic functions, including motor skills, mature first (98). Therefore, the development of early motor skills should be a priority. Parents and practitioners should provide and highlight both fine and gross motor opportunities in order to facilitate the EF of young children with ASD.
患有 ASD 的儿童经常在各个领域出现缺陷,这些缺陷会产生长期后果。运动技能困难会给孩子带来额外的负担,并可能严重影响他们的健康、日常生活和社交互动。因此,评估和了解精细和粗大运动技能的作用可能有助于父母和专业人士确定可以在早期干预以改善 EF 的技能和计划,这也可能有助于为这些患有 ASD 的幼儿提供在其发展轨迹中充分发挥潜力。目前的发现为与 ASD 幼儿打交道的父母和从业者提供了一些重要的实际意义。父母和从业者应该意识到运动技能(即精细和粗大运动技能)和 EF(即工作记忆和抑制)之间的特定关系。这种特定的关联可能表明,鉴于观察到的运动技能和 EF 之间的联系,运动技能的早期测量可能对儿童的高阶认知发展特别有益。神经影像学证据表明,与更多基本功能(包括运动技能)相关的大脑区域首先成熟 ( 98)。因此,早期运动技能的发展应该是优先事项。父母和从业者应提供并强调精细和粗大运动机会,以促进 ASD 幼儿的 EF。
While this study has yielded meaningful findings with regard to the cross-cultural associations between parental rating of motor skills and EF of young children with ASD from Taiwan and the US, several limitations need to be considered. First, the severity level, IQ, and comorbidity status of the children with ASD from both countries were not reported in this study. Although various confounding variables were included in our analyses, it is important to mention that other variables that did not account for in the present study might have played a role, given that multiple systems would influence child development (99). Second, the motor skills and EF measurement of children with ASD were assessed via parental proxy report. Such subjective rating may be influenced by personal and cultural biases or beliefs, as well as prior experiences. In order words, parental perceptions might result in different bars in evaluating their child’s daily performance of motor skills and EF (32). It is worth noting that parent rating and performance-based measurement should not be used interchangeably as they capture different aspects; preferably using these two types of assessment in combination in the best-case scenario. Therefore, future research should utilize a combination of both parental reports and objective performance-based assessments of motor skills and EF to obtain more comprehensive and detailed information regarding the relationship between motor skills and EF among young children with ASD. Another limitation to note is the representativeness of our samples. The children with ASD included in this study were recruited through specific channels, which might not necessarily reflect a nationally representative sample of children with autism in the US and Taiwan. Consequently, while our findings provide meaningful insights, they may not be definitive. Instead, they should be viewed as an initial step in understanding potential cultural differences in parental ratings of motor skills and EF among children with ASD. This study lays the groundwork for further exploration in this area, but care should be taken in extrapolating the results to broader populations. Future cross-cultural studies would greatly benefit from recruitment strategies that ensure a more nationally representative sample, enhancing the generalizability and depth of the findings. Further, the current study did not recruit children without ASD as comparison groups, which might limit our ability to understand whether specific factors contribute to cross-cultural differences between children with and without ASD. In our analysis, it’s important to note that R2 statistics are influenced by the variability present in the dataset. Higher R2 values can result from datasets with greater variability, which may not necessarily imply a stronger model fit. Throughout the regression results section, we reported adjusted R2 values to account for the number of predictors in our models. It is also important to acknowledge the exploratory nature of our analyses, where we examined various relationships between motor skills and EF without a strict set of a priori hypotheses. This approach allowed us to explore potential associations comprehensively but also comes with the inherent risk of inflated Type 1 errors. To help account for this, we used an adjusted alpha level of 0.01 to control for the error rate across multiple tests. However, given the extensive nature of our analyses, we acknowledge the potential for inflated Type 1 errors, and readers should interpret the findings in light of this exploratory approach. While the present study provides valuable insights into the relationships under investigation, we also recognize the need for future research to confirm and replicate these findings. Lastly, the cross-sectional nature of the current study limits causal implications. Future studies should examine the motor and cognitive development of children with ASD using longitudinal design and assessments to gain more insight regarding how the relationship between motor skills and EF changes over time in the ASD population.
虽然这项研究在父母对台湾和美国 ASD 幼儿的运动技能评分与 EF 之间的跨文化关联方面产生了有意义的发现,但需要考虑一些局限性。首先,本研究未报告来自这两个国家的 ASD 儿童的严重程度、智商和合并症状态。尽管我们的分析中包括各种混杂变量,但重要的是要提到,鉴于多个系统会影响儿童发展,本研究中未考虑的其他变量可能也起了作用 ( 99)。其次,通过父母代理报告评估 ASD 儿童的运动技能和 EF 测量。这种主观评级可能受到个人和文化偏见或信仰以及先前经验的影响。换句话说,父母的看法可能会导致在评估孩子的日常运动技能和 EF 表现时出现不同的标准 ( 32)。值得注意的是,家长评分和基于绩效的衡量标准不应互换使用,因为它们涵盖不同的方面;最好在最佳情况下结合使用这两种类型的评估。因此,未来的研究应结合父母报告和基于客观表现的运动技能和 EF 评估,以获得有关 ASD 幼儿运动技能与 EF 之间关系的更全面和详细的信息。另一个需要注意的限制是我们样本的代表性。本研究中包括的 ASD 儿童是通过特定渠道招募的,这可能不一定反映美国和台湾具有全国代表性的自闭症儿童样本。 因此,虽然我们的研究结果提供了有意义的见解,但它们可能不是决定性的。相反,它们应被视为了解 ASD 儿童父母对运动技能和 EF 评分的潜在文化差异的第一步。这项研究为该领域的进一步探索奠定了基础,但在将结果外推到更广泛的人群时应注意。未来的跨文化研究将极大地受益于确保更具全国代表性的样本的招募策略,从而提高研究结果的普遍性和深度。此外,目前的研究没有招募没有 ASD 的儿童作为对照组,这可能会限制我们了解特定因素是否会导致 ASD 和非 ASD 儿童之间跨文化差异的能力。在我们的分析中,需要注意的是 R 2 统计数据受数据集中存在的可变性的影响。具有较大可变性的数据集可能会导致较高的 R 2 值,这可能并不一定意味着模型拟合更强。在整个回归结果部分,我们报告了调整后的 R 2 值,以说明模型中的预测变量数量。承认我们分析的探索性也很重要,我们在没有一套严格的先验假设的情况下研究了运动技能和 EF 之间的各种关系。这种方法使我们能够全面探索潜在的关联,但也伴随着 1 型错误膨胀的固有风险。为了帮助解决这个问题,我们使用了调整后的 alpha 水平 0.01 来控制多个测试中的错误率。 然而,鉴于我们分析的广泛性,我们承认可能存在夸大的 1 型错误,读者应根据这种探索性方法来解释研究结果。虽然本研究为所调查的关系提供了有价值的见解,但我们也认识到需要未来的研究来证实和复制这些发现。最后,当前研究的横断面性质限制了因果关系。未来的研究应使用纵向设计和评估来检查 ASD 儿童的运动和认知发展,以更深入地了解 ASD 人群运动技能和 EF 之间的关系如何随时间变化。
Conclusion 结论
This research is one of the first study to explore cross-cultural relationships between motor skills and EF of young children with ASD from Taiwan and the US. Overall results revealed that parent ratings of fine motor skills and gross motor skills were significantly associated with EF ratings in both working memory and inhibition among 4–6 years children with ASD from Taiwan and the US. Further, these associations between motor skills (i.e., fine motor and gross motor skills) and EF (i.e., working memory and inhibition) ratings were similar between the two countries. The present study is the important first step in understanding the relationships between motor skills and EF development. This study also sheds light on the importance of developing relevant initiatives and programs to create motor skills and EF intervention to build the early foundation for success later in school and in life among children with ASD.
这项研究是探索台湾和美国 ASD 幼儿运动技能与 EF 之间跨文化关系的首批研究之一。总体结果显示,在来自台湾和美国的 4-6 岁 ASD 儿童中,父母对精细运动技能和粗大运动技能的评分与工作记忆和抑制的 EF 评分显著相关。此外,这两个国家的运动技能 (即精细运动和粗大运动技能) 和 EF (即工作记忆和抑制) 评级之间的这些关联相似。本研究是理解运动技能和 EF 发展之间关系的重要第一步。这项研究还阐明了制定相关举措和计划以培养运动技能和 EF 干预的重要性,以便为 ASD 儿童以后在学校和生活中的成功奠定早期基础。
Data availability statement
数据可用性声明
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary materials, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
研究中介绍的原始贡献包含在文章/补充材料中,进一步查询可直接联系通讯作者。
Ethics statement 道德声明
The studies involving humans were approved by the Institutional Review Board at Oregon State University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The informed consent was obtained from the participants.
涉及人类的研究得到了俄勒冈州立大学机构审查委员会的批准。这些研究是根据当地立法和机构要求进行的。获得参与者的知情同意。
Author contributions 作者贡献
M-CS: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. MMM: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. WM: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. SL: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. MM: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
M-CS:概念化、形式分析、调查、方法、项目管理、写作 - 原稿。MMM:概念化,写作 - 审查和编辑。WM: 概念化、写作 – 审查和编辑。SL:概念化、写作 - 审查和编辑。MM: 概念化、方法论、监督、写作 - 审查和编辑。
Funding 资金
The author (s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
作者声明,本文的研究、作者身份和/或出版未收到任何财务支持。
Acknowledgments 确认
The authors express their sincere gratitude to all the participants who participated in this study. We extend our appreciation to the ASD-organization, pediatric services, and schools in both Taiwan and the US for their assistance in facilitating the recruitment process. A special acknowledgment is reserved for Dr. Sara Rosenblum, whose gracious permission granted us access to ChAS-P.
作者对所有参与本研究的参与者表示衷心的感谢。我们感谢台湾和美国的 ASD 组织、儿科服务和学校在促进招聘过程中提供的帮助。特别感谢 Sara Rosenblum 博士,她的慷慨许可授予我们访问 ChAS-P。
Conflict of interest 利益冲突
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
作者声明,该研究是在没有任何可能被解释为潜在利益冲突的商业或财务关系的情况下进行的。
Publisher’s note 出版商的说明
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
本文中表达的所有声明仅代表作者的观点,并不一定代表其附属组织或出版商、编辑和审稿人的观点。本文中可能评估的任何商品或制造商可能提出的声明均不受出版商的保证或认可。
Footnotes 脚注
References 引用
1. Irwin, LG, Siddiqi, A, and Hertzman, G. Early child development: a powerful equalizer [internet]. Vancouver, BC: Human Early Learning Partnership (HELP) (2007).
1. Irwin, LG, Siddiqi, A 和 Hertzman, G.儿童早期发展:一个强大的均衡器 [互联网]。不列颠哥伦比亚省温哥华:人类早期学习伙伴关系 (HELP)(2007 年)。
2. McClelland, MM, and Cameron, CE. Self-regulation in early childhood: improving conceptual clarity and developing ecologically valid measures: self-regulation in early childhood: improving conceptual clarity and measures. Child Dev Perspect. (2012) 6:136–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-8606.2011.00191.x
2. McClelland, MM, 和 Cameron, CE。幼儿期的自我调节:提高概念的清晰度并开发生态有效的措施:幼儿期的自我调节:提高概念的清晰度和措施。子开发透视。(2012) 6:136–42.doi: 10.1111/j.1750-8606.2011.00191.x
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
3. Hart, JE, and Whalon, K. Misbehavior or missed opportunity? Challenges in interpreting the behavior of young children with autism Spectrum disorder. Early Childhood Educ J. (2013) 41:257–63. doi: 10.1007/s10643-012-0527-8
3. Hart, JE 和 Whalon, K. 行为不端还是错失机会?解释自闭症谱系障碍幼儿行为的挑战。幼儿教育杂志 (2013) 41:257-63。doi: 10.1007/s10643-012-0527-8
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
4. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association (2013).
4. 美国精神病学协会。精神障碍诊断与统计手册。第 5 版。华盛顿特区:美国精神病学协会(2013 年)。
5. CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020). Data and Statistics on autism Spectrum disorder | CDC. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/data.html (Accessed September 12, 2020).
5. 疾病预防控制中心。疾病控制和预防中心。(2020). 自闭症谱系障碍的数据和统计 |网址:https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/data.html(2020 年 9 月 12 日访问)。
6. Maenner, MJ. Prevalence of autism Spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years — autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2016. MMWR Surveill Summ. (2020) 69. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/69/ss/ss6904a1.htm (Accessed September 12, 2020).
6. 梅纳,MJ。自闭症谱系障碍患病率 8 岁儿童 — 自闭症和发育障碍监测网络,11 个站点,美国,2016 年。MMWR 监视总和。(2020) 69.网址:https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/69/ss/ss6904a1.htm(2020 年 9 月 12 日访问)。
7. Ministry of Health and Welfare. 統計處. 統計處; (2020). Statistics on the number of people with disabilities. Available at: https://dep.mohw.gov.tw/DOS/lp-4646-113.html (Accessed October 19, 2020)
7. 卫生和福利部。統計處.統計處;(2020). 残疾人人数统计.见:https://dep.mohw.gov.tw/DOS/lp-4646-113.html(2020 年 10 月 19 日访问)
8. U.S. Department of Education, Office of special education and rehabilitative services, Office of special education programs, 41st annual report to congress on the implementation of the individuals with disabilities education act, 2019. Washington, DC: (2020).
8. 美国教育部,特殊教育和康复服务办公室,特殊教育计划办公室,2019 年向国会提交的关于实施《残疾人教育法》的第 41 份年度报告。华盛顿特区:(2020 年)。
9. Staples, KL, and Reid, G. Fundamental movement skills and autism Spectrum disorders. J Autism Dev Disord. (2010) 40:209–17. doi: 10.1007/s10803-009-0854-9
9. Staples, KL 和 Reid, G. 基本运动技能和自闭症谱系障碍。J 自闭症 Dev Disord。(2010) 40:209–17.doi: 10.1007/s10803-009-0854-9
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
10. Whyatt, CP, and Craig, CM. Motor skills in children aged 7–10 years, diagnosed with autism Spectrum disorder. J Autism Dev Disord. (2012) 42:1799–809. doi: 10.1007/s10803-011-1421-8
10. Whyatt, CP 和 Craig, CM. 被诊断患有自闭症谱系障碍的 7-10 岁儿童的运动技能。J 自闭症 Dev Disord。(2012) 42:1799–809.doi: 10.1007/s10803-011-1421-8
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
11. Robinson, L, Stodden, DF, Barnett, LM, Lopes, VP, Logan, SW, Rodrigues, LP, et al. Motor competence and its effect on positive developmental trajectories of health. Sports Med. (2015) 45:1273–84. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0351-6
11. Robinson, L, Stodden, DF, Barnett, LM, Lopes, VP, Logan, SW, Rodrigues, LP 等。运动能力及其对健康积极发展轨迹的影响。运动医学 (2015) 45:1273-84。doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0351-6
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
12. Green, D, Charman, T, Pickles, A, Chandler, S, Loucas, T, Simonoff, E, et al. Impairment in movement skills of children with autistic spectrum disorders. Dev Med Child Neurol. (2009) 51:311–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.03242.x
12. Green, D, Charman, T, Pickles, A, Chandler, S, Loucas, T, Simonoff, E 等人。自闭症谱系障碍儿童运动技能受损。Dev Med 儿童神经学。(2009) 51:311-6。doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.03242.x
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
13. Lloyd, M, Mac Donald, M, and Lord, C. Motor skills of toddlers with autism spectrum disorders. Autism. (2013) 17:133–46. doi: 10.1177/1362361311402230
13. Lloyd, M, Mac Donald, M, 和 Lord, C. 自闭症谱系障碍幼儿的运动技能。孤独症。(2013) 17:133–46.doi: 10.1177/1362361311402230
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
14. Pan, CY. Motor proficiency and physical fitness in adolescent males with and without autism spectrum disorders. Autism. (2014) 18:156–65. doi: 10.1177/1362361312458597
14. 潘,CY。患有和不患有自闭症谱系障碍的青少年男性的运动熟练度和身体素质。孤独症。(2014) 18:156–65.doi: 10.1177/1362361312458597
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
15. Van Damme, T, Vancampfort, D, Thoen, A, CPR, S, and Van Biesen, D. Evaluation of the developmental coordination questionnaire (DCDQ) as a screening instrument for co-occurring motor problems in children with autism Spectrum disorder. J Autism Dev Disord. (2022 [) 52:4079–88. doi: 10.1007/s10803-021-05285-1
15. Van Damme, T, Vancampfort, D, Thoen, A, CPR, S 和 Van Biesen, D. 评估发育协调问卷 (DCDQ) 作为自闭症谱系障碍儿童同时发生的运动问题的筛查工具。J 自闭症 Dev Disord。(2022 [) 52:4079–88. doi: 10.1007/s10803-021-05285-1
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
16. Bhat, AN. Is motor impairment in autism Spectrum disorder distinct from developmental coordination disorder? A report from the SPARK study. Phys Ther. (2020) 100:633–44. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzz190
16. 巴特,安那州。自闭症谱系障碍的运动障碍与发育协调障碍不同吗?来自 SPARK 研究的报告。物理学。(2020) 100:633–44.doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzz190
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
17. Landa, R, and Garrett-Mayer, E. Development in infants with autism spectrum disorders: a prospective study. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. (2006) 47:629–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01531.x
17. Landa, R 和 Garrett-Mayer, E. 自闭症谱系障碍婴儿的发育:一项前瞻性研究。J 儿童心理学精神病学。(2006) 47:629–38.doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01531.x
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
18. West, KL. Infant motor development in autism Spectrum disorder: a synthesis and Meta-analysis. Child Dev. (2019) 90:2053–70. doi: 10.1111/cdev.13086
18. West, KL. 自闭症谱系障碍的婴儿运动发育:综合和荟萃分析。儿童发展 (2019) 90:2053-70。doi: 10.1111/cdev.13086
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
19. Chen, SF, Chien, YL, Wu, CT, Shang, CY, Wu, YY, and Gau, SS. Deficits in executive functions among youths with autism spectrum disorders: an age-stratified analysis. Psychol Med. (2016) 46:1625–38. doi: 10.1017/S0033291715002238
19. Chen, SF, Chien, YL, Wu, CT, Shang, CY, Wu, YY, and Gau, SS. 自闭症谱系障碍青少年执行功能缺陷:年龄分层分析。心理学医学 (2016) 46:1625-38。doi: 10.1017/S0033291715002238
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
20. Hill, EL. Executive dysfunction in autism. Trends Cogn Sci. (2004) 8:26–32. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2003.11.003
20. 希尔,EL。自闭症的执行功能障碍。趋势认知科学 (2004) 8:26-32。doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2003.11.003
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
21. Diamond, A. Executive functions. Annu Rev Psychol. (2013) 64:135–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750
21. 戴蒙德,A. 执行功能。Annu Rev Psychol. (2013) 64:135-68。doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
22. Corbett, BA, Constantine, LJ, Hendren, R, Rocke, D, and Ozonoff, S. Examining executive functioning in children with autism spectrum disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and typical development. Psychiatry Res. (2009) 166:210–22. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2008.02.005
22. Corbett, BA, Constantine, LJ, Hendren, R, Rocke, D, 和 Ozonoff, S. 检查自闭症谱系障碍、注意力缺陷多动障碍和典型发展儿童的执行功能。精神病学研究 (2009) 166:210-22。doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2008.02.005
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
23. Demetriou, EA, Lampit, A, Quintana, DS, Naismith, SL, Song, YJC, Pye, JE, et al. Autism spectrum disorders: a meta-analysis of executive function. Mol Psychiatry. (2018) 23:1198–204. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.75
23. Demetriou, EA, Lampit, A, Quintana, DS, Naismith, SL, Song, YJC, Pye, JE 等人。自闭症谱系障碍:执行功能的荟萃分析。摩尔精神病学。(2018) 23:1198–204.DOI: 10.1038/MP.2017.75
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
24. Ozonoff, S, and Jensen, J. Brief report: specific executive function profiles in three neurodevelopmental disorders. J Autism Dev Disord. (1999) 29:171–7. doi: 10.1023/A:1023052913110
24. Ozonoff, S 和 Jensen, J. 简要报告:三种神经发育障碍的特定执行功能概况。J 自闭症 Dev Disord。(1999) 29:171–7.doi: 10.1023/A:1023052913110
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
25. Zhang, Z, Peng, P, and Zhang, D. Executive function in high-functioning autism Spectrum disorder: a Meta-analysis of fMRI studies. J Autism Dev Disord. (2020 [) Available from: 50:4022–38. doi: 10.1007/s10803-020-04461-z
25. Zhang, Z, Peng, P, and Zhang, D. 高功能自闭症谱系障碍的执行功能:fMRI 研究的荟萃分析。J 自闭症 Dev Disord。(2020 [) 可从:50:4022–38. doi: 10.1007/s10803-020-04461-z
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
26. Robinson, S, Goddard, L, Dritschel, B, Wisley, M, and Howlin, P. Executive functions in children with autism Spectrum disorders. Brain Cogn. (2009) 71:362–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2009.06.007
26. Robinson, S, Goddard, L, Dritschel, B, Wisley, M, 和 Howlin, P. 自闭症谱系障碍儿童的执行功能。Brain Cogn. (2009) 71:362-8。doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2009.06.007
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
27. Best, JR, and Miller, PH. A developmental perspective on executive function. Child Dev. (2010) 81:1641–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2010.01499.x
27. Best , JR 和 Miller, PH。执行功能的发展观点。儿童开发 (2010) 81:1641-60。doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2010.01499.x
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
28. Hume, K, Loftin, R, and Lantz, J. Increasing Independence in autism Spectrum disorders: a review of three focused interventions. J Autism Dev Disord. (2009) 39:1329–38. doi: 10.1007/s10803-009-0751-2
28. Hume, K, Loftin, R, 和 Lantz, J. 提高自闭症谱系障碍的独立性:三种重点干预措施的回顾。J 自闭症 Dev Disord。(2009) 39:1329–38.doi: 10.1007/s10803-009-0751-2
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
29. Woolard, A, Stratton, E, Demetriou, EA, Boulton, KA, Pellicano, E, Glozier, N, et al. Perceptions of social and work functioning are related to social anxiety and executive function in autistic adults. Autism. (2021) 25:2124–34. doi: 10.1177/13623613211013664
29. Woolard, A, Stratton, E, Demetriou, EA, Boulton, KA, Pellicano, E, Glozier, N, et al.对社交和工作功能的看法与自闭症成人的社交焦虑和执行功能有关。孤独症。(2021) 25:2124–34.doi: 10.1177/13623613211013664
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
30. Hertzberg, OE. The relationship of motor ability to the intelligence of kindergarten children. J Educ Psychol. (1929) 20:507–19. doi: 10.1037/h0070410
30. 赫茨伯格,俄勒冈州。运动能力与幼儿园儿童智力的关系。J Educ Psychol. (1929) 20:507-19。doi: 10.1037/h0070410
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
31. Becker, DR, Miao, A, Duncan, R, and McClelland, MM. Behavioral self-regulation and executive function both predict visuomotor skills and early academic achievement. Early Child Res Q. (2014) 29:411–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ecresq.2014.04.014
31. Becker, DR, Miao, A, Duncan, R, and McClelland, MM. 行为自我调节和执行功能都可以预测视觉运动技能和早期学业成绩。早期儿童研究 Q. (2014) 29:411-24。doi: 10.1016/j.ecresq.2014.04.014
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
32. Houwen, S, van der Veer, G, Visser, J, and Cantell, M. The relationship between motor performance and parent-rated executive functioning in 3- to 5-year-old children: what is the role of confounding variables? Hum Mov Sci. (2017) 53:24–36. doi: 10.1016/j.humov.2016.12.009
32. Houwen, S, van der Veer, G, Visser, J, 和 Cantell, M.3 至 5 岁儿童运动表现与父母评定的执行功能之间的关系:混杂变量的作用是什么?Hum Mov Sci. (2017) 53:24-36。doi: 10.1016/j.humov.2016.12.009
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
PubMed 摘要 |CrossRef 全文 |谷歌学术
33. Mac Donald, M, Lipscomb, S, McClelland, MM, Duncan, R, Becker, D, Anderson, K, et al. Relations of preschoolers’ visual-motor and object manipulation skills with executive function and social behavior. Res Q Exerc Sport. (2016) 87:396–407. doi: 10.1080/02701367.2016.1229862
33. Mac Donald, M, Lipscomb, S, McClelland, MM, Duncan, R, Becker, D, Anderson, K, et al.学龄前儿童的视觉运动和物体作技能与执行功能和社会行为的关系。Res Q Exerc Sport.(2016) 87:396–407.doi: 10.1080/02701367.2016.1229862
34. van der Fels, IMJ, te Wierike, SCM, Hartman, E, Elferink-Gemser, MT, Smith, J, and Visscher, C. The relationship between motor skills and cognitive skills in 4–16 year old typically developing children: a systematic review. J Sci Med Sport. (2015) 18:697–703. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2014.09.007
35. Hilton, CL, Cumpata, K, Klohr, C, Gaetke, S, Artner, A, Johnson, H, et al. Effects of exergaming on executive function and motor skills in children with autism Spectrum disorder: a pilot study. Am J Occup Ther. (2014) 68:57–65. doi: 10.5014/ajot.2014.008664
36. Schurink, J, Hartman, E, Scherder, EJA, Houwen, S, and Visscher, C. Relationship between motor and executive functioning in school-age children with pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified. Res Autism Spectr Disord. (2012) 6:726–32. doi: 10.1016/j.rasd.2011.10.013
37. Gibbs, RW Jr. Embodiment and cognitive science, vol. 347. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press (2005).
38. Piaget, J. The origins of intelligence in children In: M Cook, editor. The origins of intelligence in children. New York, NY, US: W W Norton & Co (1952). 419.
39. Smith, L, and Gasser, M. The development of embodied cognition: six lessons from babies. Artif Life. (2005) 11:13–29. doi: 10.1162/1064546053278973
40. Adolph, KE. Learning to learn in the development of action In: IJJ Rieser, JJ Lockman, and CA Nelson, editors. Action as an organizer of learning and development. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum (2005). 91–122.
41. Diamond, A. Close interrelation of motor development and cognitive development and of the cerebellum and prefrontal cortex. Child Dev. (2000) 71:44–56. doi: 10.1111/1467-8624.00117
42. Anderson, P. Assessment and development of executive function (EF) during childhood. Child Neuropsychol. (2002) 8:71–82. doi: 10.1076/chin.8.2.71.8724
43. Venetsanou, F, and Kambas, A. Environmental factors affecting preschoolers’ motor development. Early Childhood Educ J. (2010) 37:319–27. doi: 10.1007/s10643-009-0350-z
44. Chow, SMK, Henderson, SE, and Barnett, AL. The movement assessment battery for children: a comparison of 4-year-old to 6-year-old children from Hong Kong and the United States. Am J Occup Ther. (2001) 55:55–61. doi: 10.5014/ajot.55.1.55
45. Lan, X, Legare, CH, Ponitz, CC, Li, S, and Morrison, FJ. Investigating the links between the subcomponents of executive function and academic achievement: a cross-cultural analysis of Chinese and American preschoolers. J Exp Child Psychol. (2011) 108:677–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jecp.2010.11.001
46. Chow, SMK, Hsu, YW, Henderson, SE, Barnett, AL, and Lo, SK. The movement ABC: a cross-cultural comparison of preschool children from Hong Kong, Taiwan, and the USA. Adapt Phys Act Q. (2006) 23:31–48. doi: 10.1123/apaq.23.1.31
47. Schmitt, SA, Korucu, I, Purpura, DJ, Whiteman, S, Zhang, C, and Yang, F. Exploring cross-cultural variations in the development of executive function for preschoolers from low and high socioeconomic families. Int J Behav Dev. (2019) 43:212–20. doi: 10.1177/0165025418785469
48. Sabbagh, MA, Xu, F, Carlson, SM, Moses, LJ, and Lee, K. The development of executive functioning and theory of mind: a comparison of Chinese and U.S. Preschool Psychol Sci. (2006) 17:74–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2005.01667.x
49. Livesey, D, Keen, J, Rouse, J, and White, F. The relationship between measures of executive function, motor performance and externalising behaviour in 5- and 6-year-old children. Hum Mov Sci. (2006) 25:50–64. doi: 10.1016/j.humov.2005.10.008
50. Ludyga, S, Pühse, U, Gerber, M, and Herrmann, C. Core executive functions are selectively related to different facets of motor competence in preadolescent children. Eur J Sport Sci. (2019) 19:375–83. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2018.1529826
51. Piek, JP, Dyck, MJ, Nieman, A, Anderson, M, Hay, D, Smith, LM, et al. The relationship between motor coordination, executive functioning and attention in school aged children. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. (2004) 19:1063–76. doi: 10.1016/j.acn.2003.12.007
52. Kim, H, Carlson, AG, Curby, TW, and Winsler, A. Relations among motor, social, and cognitive skills in pre-kindergarten children with developmental disabilities. Res Dev Disabil. (2016) 53-54:43–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2016.01.016
53. Ramello de Carvalho, AC, Quintas, R, Blascovi-Assis, S, and Seabra, A. Motor performance, intelligence, and executive function in children with ASD. Int J dev Res. (2020) 10:34053–60.
54. Chatterjee, SD, Moody, G, Lowry, PB, Chakraborty, S, and Hardin, A. The nonlinear influence of harmonious information technology affordance on organisational innovation. Inf Syst J. (2021) 31:294–322. doi: 10.1111/isj.12311
55. D’Aniello, C, Tambling, R, and Russell, B. The internalized stigma of substance abuse scale for caregivers: measuring substance use stigma experienced by caregivers. Alcohol Treat Q. (2022) 40:83–92. doi: 10.1080/07347324.2021.1941473
56. Rosenblum, S. The development and standardization of the children activity scales (ChAS-P/T) for the early identification of children with developmental coordination disorders. Child Care Health Dev. (2006) 32:619–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2214.2006.00687.x
57. Mimouni-Bloch, A, Offek, H, Rosenblum, S, Posener, I, Silman, Z, and Engel-Yeger, B. Association between sensory modulation and daily activity function of children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and children with typical development. Res Dev Disabil. (2018) 83:69–76. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2018.08.002
58. Asunta, P, Viholainen, H, Ahonen, T, and Rintala, P. Psychometric properties of observational tools for identifying motor difficulties – a systematic review. BMC Pediatr. (2019) 19:322. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1657-6
59. Bardid, F, Vannozzi, G, Logan, SW, Hardy, LL, and Barnett, LM. A hitchhiker’s guide to assessing young people’s motor competence: deciding what method to use. J Sci Med Sport. (2019) 22:311–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2018.08.007
60. Thorell, LB, and Nyberg, L. The childhood executive functioning inventory (CHEXI): a new rating instrument for parents and teachers. Dev Neuropsychol. (2008) 33:536–52. doi: 10.1080/87565640802101516
61. Blijd-Hoogewys, EMA, Bezemer, ML, and van Geert, PLC. Executive functioning in children with ASD: an analysis of the BRIEF. J Autism Dev Disord. (2014) 44:3089–100. doi: 10.1007/s10803-014-2176-9
62. Gioia, GA, Isquith, PK, Retzlaff, PD, and Espy, KA. Confirmatory factor analysis of the behavior rating inventory of executive function (BRIEF) in a clinical sample. Child Neuropsychol. (2002) 8:249–57. doi: 10.1076/chin.8.4.249.13513
63. Thorell, LB, Eninger, L, Brocki, KC, and Bohlin, G. Childhood executive function inventory (CHEXI): a promising measure for identifying young children with ADHD? J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. (2010) 32:38–43. doi: 10.1080/13803390902806527
64. Camerota, M, Willoughby, MT, Kuhn, LJ, and Blair, CB. The childhood executive functioning inventory (CHEXI): factor structure, measurement invariance, and correlates in US preschoolers. Child Neuropsychol. (2018) 24:322–37. doi: 10.1080/09297049.2016.1247795
65. Tsai, CL, Thorell, LB, Siu, AFY, Hsu, YH, and Lin, HL. Taiwanese traditional-Chinese childhood executive functioning inventory: revision, investigation of psychometric properties, and establishing of norms. Psychol Test. (2020) 67:119–43.
66. Van Rooijen, M, Verhoeven, L, and Steenbergen, B. Working memory and fine motor skills predict early numeracy performance of children with cerebral palsy. Child Neuropsychol. (2016) 22:735–47. doi: 10.1080/09297049.2015.1046426
67. Van Der, FIMJ, Smith, J, De, BAGM, Bosker, RJ, Königs, M, Oosterlaan, J, et al. Relations between gross motor skills and executive functions, controlling for the role of information processing and lapses of attention in 8-10 year old children. PLoS One. (2019) 14:e0224219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224219
68. Piek, JP, Dawson, L, Smith, LM, and Gasson, N. The role of early fine and gross motor development on later motor and cognitive ability. Hum Mov Sci. (2008) 27:668–81. doi: 10.1016/j.humov.2007.11.002
69. Wu, M, Liang, X, Lu, S, and Wang, Z. Infant motor and cognitive abilities and subsequent executive function. Infant Behav Dev. (2017) 49:204–13. doi: 10.1016/j.infbeh.2017.09.005
70. Hellendoorn, A, Wijnroks, L, van Daalen, E, Dietz, C, Buitelaar, JK, and Leseman, P. Motor functioning, exploration, visuospatial cognition and language development in preschool children with autism. Res Dev Disabil. (2015) 39:32–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2014.12.033
71. Hartman, E, Houwen, S, Scherder, E, and Visscher, C. On the relationship between motor performance and executive functioning in children with intellectual disabilities. J Intellect Disabil Res. (2010) 54:468–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.2010.01284.x
72. Houwen, S, Visser, L, van der Putten, A, and Vlaskamp, C. The interrelationships between motor, cognitive, and language development in children with and without intellectual and developmental disabilities. Res Dev Disabil. (2016) 53-54:19–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2016.01.012
73. Wuang, YP, Wang, CC, Huang, MH, and Su, CY. Profiles and cognitive predictors of motor functions among early school-age children with mild intellectual disabilities. J Intellect Disabil Res. (2008) 52:1048–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.2008.01096.x
74. Schott, N, and Holfelder, B. Relationship between motor skill competency and executive function in children with Down’s syndrome. J Intellect Disabil Res. (2015) 59:860–72. doi: 10.1111/jir.12189
75. Leonard, HC, Bernardi, M, Hill, EL, and Henry, LA. Executive functioning, motor difficulties, and developmental coordination disorder. Dev Neuropsychol. (2015) 40:201–15. doi: 10.1080/87565641.2014.997933
76. Ziereis, S, and Jansen, P. Correlation of motor abilities and executive functions in children with ADHD. Appl Neuropsychol Child. (2016) 5:138–48. doi: 10.1080/21622965.2015.1038746
77. Liu, T, Tongish, M, Li, Y, and Okuda, PMM. Executive and motor function in children with autism spectrum disorder. Cogn Process. (2023) 24:537–47. doi: 10.1007/s10339-023-01156-y
78. Hanakawa, T. Rostral premotor cortex as a gateway between motor and cognitive networks. Neurosci Res. (2011) 70:144–54. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2011.02.010
79. Campos, JJ, Anderson, DI, Barbu-Roth, MA, Hubbard, EM, Hertenstein, MJ, and Witherington, D. Travel broadens the mind. Infancy. (2000) 1:149–219. doi: 10.1207/S15327078IN0102_1
80. Rosenblum, S, Amit Ben-Simhon, H, Meyer, S, and Gal, E. Predictors of handwriting performance among children with autism spectrum disorder. Res Autism Spectr Disord. (2019) 60:16–24. doi: 10.1016/j.rasd.2019.01.002
81. Saint John, T, Estes, AM, Dager, SR, Kostopoulos, P, Wolff, JJ, Pandey, J, et al. Emerging executive functioning and motor development in infants at high and low risk for autism Spectrum disorder. Front Psychol. (2016) 7:1016. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01016
82. Cameron, CE, Brock, LL, Murrah, WM, Bell, LH, Worzalla, SL, Grissmer, D, et al. Fine motor skills and executive function both contribute to kindergarten achievement. Child Dev. (2012) 83:1229–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2012.01768.x
83. Pitchford, NJ, Papini, C, Outhwaite, LA, and Gulliford, A. Fine motor skills predict Maths ability better than they predict Reading ability in the early primary school years. Front Psychol. (2016) 7:783. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00783
84. Lehmann, J, Quaiser-Pohl, C, and Jansen, P. Correlation of motor skill, mental rotation, and working memory in 3- to 6-year-old children. Eur J Dev Psychol. (2014) 11:560–73. doi: 10.1080/17405629.2014.888995
85. Rigoli, D, Piek, JP, Kane, R, and Oosterlaan, J. An examination of the relationship between motor coordination and executive functions in adolescents. Dev Med Child Neurol. (2012) 54:1025–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2012.04403.x
86. Wassenberg, R, Feron, FJM, Kessels, AGH, Hendriksen, JGM, Kalff, AC, Kroes, M, et al. Relation between cognitive and motor performance in 5- to 6-year-old children: results from a large-scale cross-sectional study. Child Dev. (2005) 76:1092–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2005.00899.x
87. Grodd, W, Hülsmann, E, Lotze, M, Wildgruber, D, and Erb, M. Sensorimotor mapping of the human cerebellum: fMRI evidence of somatotopic organization. Hum Brain Mapp. (2001) 13:55–73. doi: 10.1002/hbm.1025
88. Marvel, CL, and Desmond, JE. Functional topography of the cerebellum in verbal working memory. Neuropsychol Rev. (2010) 20:271–9. doi: 10.1007/s11065-010-9137-7
89. Sung, MC, Ku, B, Leung, W, and Mac, DM. The effect of physical activity interventions on executive function among people with neurodevelopmental disorders: a Meta-analysis. J Autism Dev Disord. (2022) 52:1030–50. doi: 10.1007/s10803-021-05009-5
90. Best, JR, Miller, PH, and Jones, LL. Executive functions after age 5: changes and correlates. Dev Rev. (2009) 29:180–200. doi: 10.1016/j.dr.2009.05.002
91. Holloway, JM, Long, TM, and Biasini, F. Relationships between gross motor skills and social function in young boys with autism spectrum disorder. Pediatr Phys Ther. (2018) 30:184–90. doi: 10.1097/PEP.0000000000000505
92. Pennequin, V, Sorel, O, and Fontaine, R. Motor planning between 4 and 7 years of age: changes linked to executive functions. Brain Cogn. (2010) 74:107–11. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2010.07.003
93. Pan, CY, Chu, CH, Tsai, CL, Sung, MC, Huang, CY, and Ma, WY. The impacts of physical activity intervention on physical and cognitive outcomes in children with autism Spectrum disorder. Autism. (2017) 21:190–202. doi: 10.1177/1362361316633562
94. Tsai, CL, Wang, CH, and Tseng, YT. Effects of exercise intervention on event-related potential and task performance indices of attention networks in children with developmental coordination disorder. Brain Cogn. (2012) 79:12–22. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2012.02.004
95. Maurer, MN, and Roebers, CM. Towards a better understanding of the association between motor skills and executive functions in 5- to 6-year-olds: the impact of motor task difficulty. Hum Mov Sci. (2019) 66:607–20. doi: 10.1016/j.humov.2019.06.010
96. Davare, M, Andres, M, Cosnard, G, Thonnard, JL, and Olivier, E. Dissociating the role of ventral and dorsal premotor cortex in precision grasping. J Neurosci. (2006) 26:2260–8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3386-05.2006
97. Luo, Z, Jose, PE, Huntsinger, CS, and Pigott, TD. Fine motor skills and mathematics achievement in east Asian American and European American kindergartners and first graders. Br J Dev Psychol. (2007) 25:595–614. doi: 10.1348/026151007X185329
98. Casey, BJ, Tottenham, N, Liston, C, and Durston, S. Imaging the developing brain: what have we learned about cognitive development? Trends Cogn Sci. (2005) 9:104–10. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2005.01.011
Keywords: motor abilities, cognitive function, preschool children, cross-cultural study, autism
Citation: Sung M-C, McClelland MM, Massey W, Logan SW and MacDonald M (2024) Association between motor skills and executive function of children with autism spectrum disorder in Taiwan and the United States. Front. Public Health. 11:1292695. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1292695
Edited by:
Liane Beretta De Azevedo, University of Huddersfield, United KingdomReviewed by:
Gabriel Barg, Catholic University of Uruguay, UruguayJohn Stephenson, University of Huddersfield, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2024 Sung, McClelland, Massey, Logan and MacDonald. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ming-Chih Sung, msung@uscupstate.edu
 Ming-Chih Sung
Ming-Chih Sung Megan M. McClelland
Megan M. McClelland William Massey
William Massey Samuel W. Logan
Samuel W. Logan Megan MacDonald
Megan MacDonald